For family planning
Prvi korak u planiranju trudnoće i porodice.
ENVISION carrier screening test daje najpouzdanije i najdetaljnije informacije o zdravlju buduće porodice
Šta je ENVISION
carrier screening test?
Envision carrier screening otkriva da li vi i vaš partner nosite izmenjene gene koje možete preneti na vaše dete.
Ako dete izmenjen gen nasledi od oba roditelja dolazi do razvoja ozbiljnih genetskih poremećaja poput cistične fibroze, spinalne mišićne atrofije, teških hematoloških oboljenja.
Većina ljudi su nosioci skrivenih promena u strukturi gena, a da to ne znaju.
Ove promene ne utiču na vaše zdravlje ali je vaše dete u povišenom riziku za razvoj bolesti.
Zbog načina nasleđivanja ovih poremećaja nemoguće je predvideti koji roditelji će i u kojoj trudnoći dobiti bolesno dete.
Sprečavanje bolesti koje se autozomno recesivno i X vezano recesivno nasleđuju moguće je jedino utvrđivanjem statusa nosioca gena odnosno carrier screening testom.


RIZICI KOJE NE PREPOZNAJEMO
 dece sa genetskim poremećajem rođeno je od roditelja koji nemaju porodičnu istoriju bolesti ili simptome poremećaja.
dece sa genetskim poremećajem rođeno je od roditelja koji nemaju porodičnu istoriju bolesti ili simptome poremećaja.

1 od 4 osobe je nosilac gena za barem jednu bolest.*
* Klinička studija Lazarin et al (2011.)
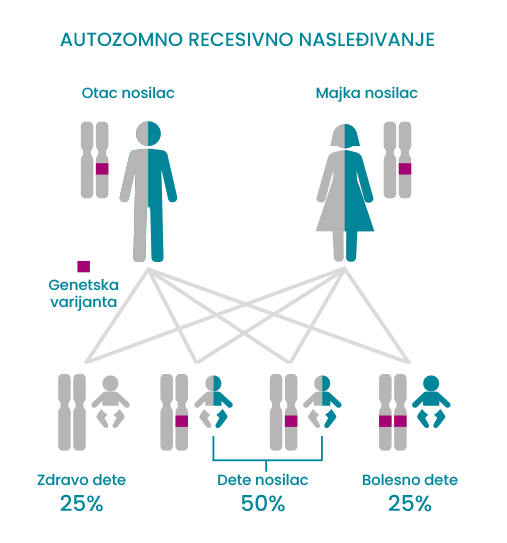
Autozomno recesivno nasleđivanje podrazumeva da osoba mora naslediti izmenjen gen od oba roditelja da bi imala razvijenu bolest.
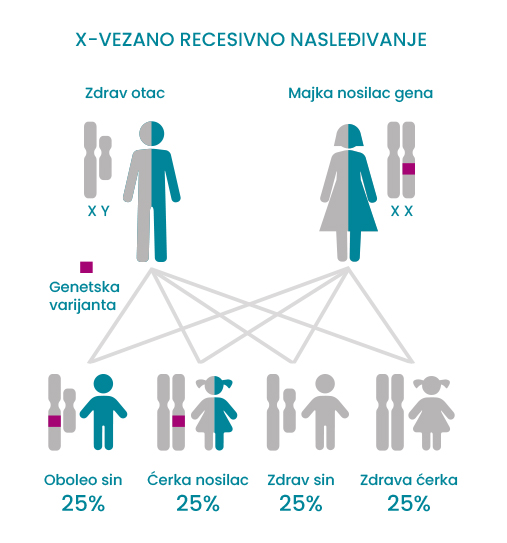
X-vezano recesivno nasleđivanje podrazumeva da se gen nalazi na X hromozomu.
Žene nosioci obično nemaju simptome jer poseduju funkcionalnu kopiju gena na drugom X hromozomu.
S obzirom na to da muškarci imaju jedan X hromozom ukoliko naslede mutiran gen znači da će biti pogođeni bolešću
Zdravlje vaše bebe je u vašim genima.
Kada planirate život i budućnost sa Vašim partnerom, fantastično je da imate što više sličnosti.
Međutim, kada su u pitanju vaši geni, različitosti su poželjne i dobre.

Kome je namenjen ENVISION
carrier screening test?


Parovima koji planiraju porodicu

Parovima u ranoj trudnoći
Ukoliko do sada niste uradili Envision carrier screening test, možete ga uraditi sada a informacije koje dobijete odnose se na ovu i svaku narednu trudnoću.

Parovima koji prolaze kroz proces vantelesne oplodnje i/ili su imali neuspeli pokušaj vantelesne oplodnje
Kada prolazite kroz ovaj u isto vreme komplikovan i lep proces važno je da uradite sve kako biste rizik od neuspeha sveli na minimum.

Osobama koje u porodici imaju genetska oboljenja
Kada imate primer genetske bolesti u porodici morate proveriti da li je i u kolikom riziku od nasleđivanja Vaše dete.

Određenim etničkim grupama koje su u povišenom riziku za genetska oboljenja
Neke grupe stanovništva dokazano imaju veću učestalost genetskih oboljenja, pripadnicima tih grupa se savetuje Envision carrier screening test kao obavezan deo planiranja porodice.

Svakom pojedincu koji želi da zna da li je nosilac izmenjenih gena koji kod potomstva mogu dovesti do nekog oboljenja
Carrier screening test treba da urade sve trudnice u najranijoj trudnoći kao i sve žene koje planiraju trudnoću.
Obstet Gynecol. 2017.
Šta analizira ENVISION carrier screening test
i koju tehnologiju koristi?
Kako smo izabrali bolesti
koje ćemo analizirati?
Sve bolesti preporučene od strane američkih udruženja genetičara ACMG i ginekologa i akušera ACOG
Bolesti koje imaju tešku kliničku sliku
Bolesti koje značajno narušavaju kvalitet života pacijenata
Bolesti koje se razvijaju u prvim godinama života
Bolesti za koje je dostupno hirurško ili medikamentozno lečenje
Zahvaljujući najsavremenijoj tehnologiji analize DNK sa preciznošću preko 99% budući roditelji mogu uraditi najsveobuhvatnije analize i dobiti jasnu i preciznu sliku o zdravlju svog deteta.
Metode analiziranja gena u su full-gene sequencing uz obaveznu analizu delecija i duplikacija u regionima od značaja +/- 10 baznih parova.
Tehnologija izvođenja ove dve metode je Next generation sequencing.
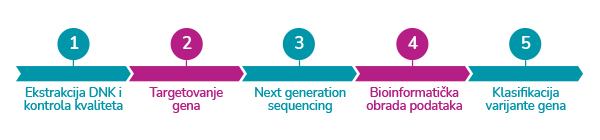
Koje korake prolazi uzorak Vaše krvi u toku analize?


Izaberite odgovarajući carrier test koji odgovara Vašim potrebama.

LIGHT PCR
PCR

![]() 2 gena
2 gena
● Cistična fibroza, F508del
● Spinalna mišićna atrofija, SMN1 gen
jedan partner
110 EUR
oba partnera
220 EUR

LIGHT NGS

![]() 2 gena
2 gena
● Spinalna mišićna atrofija, SMN1 gen
jedan partner
190 EUR
oba partnera
380 EUR

PLUS

![]() 30 gena
30 gena
spisak bolesti
jedan partner
400 EUR
oba partnera
680 EUR


![]() 400 gena
400 gena
spisak bolesti
● Kompletan i precizan uvid u preko 450 najznačajnijih monogenskih bolesti
jedan partner
550 EUR
oba partnera
935 EUR

COMPLETE

![]() 2200 gena
2200 gena
spisak bolesti
● Sveobuhvatna analiza širokog spektra genskih mutacija
jedan partner
750 EUR
oba partnera
1275 EUR
Info centar
011 414 65 65
Naručite test
Molimo Vas da unesete svoje podatke
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Rezultati i dalji koraci
Mogući rezultati ENVISION testa:
- Nisu detektovane promene na ispitivanim genima
+ Detektovane promene na ispitivanim genima
Koji su dalji koraci?
Ako ste Vi i Vaš partner nosioci izmenjenog gena,
naši genetičari će Vas posavetovati o tačnom riziku da
Vaša beba ima bolest kao i o daljim koracima koji mogu uključivati:
● Dijagnostičke testove u trudnoći – amniocentezu
ili biopsiju horionskih čupica
● Alternativne metode začeća
● PGT – M


Spisak bolesti koje analizira

| Deficit 3-Hidroksi-3-metilglutaril-CoA liaze | HMGCL |
| Deficit 3-Ketotiolaze | ACAT 1 |
| Deficit 3-Metilcrotonil-CoA karboksilaze 1 (3-MCC deficit) | MCCC1 |
| Deficit 3-Metilcrotonil-CoA karboksilaze 2 (3-MCC deficit) | MCCC2 |
| Abetalipoproteinemija | MTTP |
| Ahondrogenesis, tip IB; Atelosteogenesis II; Diastrofična displazija; Multipla epifizalna displazija | SLC26 A2 |
| Ahromatopsija | CNGB3 |
| Akrodermatitis enteropatika | SLC 39A4 |
| Deficit Acyl-CoA dehidrogenaze-9 (ACAD9) | ACAD9 |
| Deficit Adenozin deaminaze | ADA |
| Adrenalna kongenitalna insuficiencija sa 46,XY reverzijom pola, parcijalna ili kompletna | CYP 11 A1 |
| Adrenoleukodistrofija, X-vezana | ABCD1 |
| Aicardi-Goutieres sindrom | SAMHD1 |
| Aicardi-Goutieres sindrom 2 | RNASEH2B |
| Albinizam, okulokutani tip IA; Albinizam, okulokutani tip IB | TYR |
| Albinizam, okulokutani, tip II; Albinizam, smeđi okulokutani; koža/kosa/oči pigmentacija 1 | OCA2 |
| Alkaptonurija | HGD |
| Allan-Herndon-Dudley sindrom | SLC16 A2 |
| Alfa talasemija | HBA1 / HBA2 |
| Alfa-talasemija - sindrom X-vezanog intelektualnog invaliditeta | ATRX |
| Deficijencija Alfa-1 antitripsina | SERPINA1 |
| Alfa-manozidoza | MAN2B1 |
| Alport sindrom, COL4A3- vezano | COL 4 A3 |
| Alport sindrom, COL4A4- vezano | COL 4 A4 |
| Alport sindrom, COL4A5- vezano | COL 4 A5 |
| Alstrom sindrom | ALMS1 |
| Poremećaj spektra hipoplazije i anauksetične displazije hrskavice i dlake | RMRP |
| Anderman sindrom | SLC12 A6 |
| Deficit Arginaze | ARG1 |
| Deficit Argininosucinat liaze | ASL |
| Deficit Aromataze | CYP19A1 |
| SLC35A3-vezani poremećaji | SLC35A3 |
| Poremećaji povezani sa PRPS1 (uključujući Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest tip 5 i Arts sindrom) | PRPS1 |
| Deficit Asparagin sintetaze | ASNS |
| Aspartilglucozaminurija | AGA |
| Ataksija sa deficitom vitamina E | TTPA |
| Ataksija telegiekstazija | ATM |
| Atransferinemija | TF |
| Autoimuna poliendokrinopatija sa kandidijazom i ektodermalnom distorfijom | AIRE |
| Autozomno recesivna spastična ataksija Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS) | SACS |
| Leberova kongenitalna amauroza 10/povezana sa poremećajem CEP290 | CEP290 |
| Bardet-Biedl sindrom (BBS2-vezan) | BBS2 |
| Bardet-Biedl sindrom tip 1 | BBS1 |
| Bardet-Biedl sindrom tip 10 | BBS10 |
| Bardet-Biedl sindrom tip 12 | BBS12 |
| Glavni nedostatak kompleksa histokompatibilnosti klase II ( CIITA-vezano) | CIITA |
| Bartter sindrom tip IV (BSND-vezan) | BSND |
| Bernard-Soulier sindorm (GP1BA-vezano) | GP1BA |
| Bernard-Soulier sindrom (GP9-vezano) | GP9 |
| Polimikrogirija (ADGRG1-vezano) | ADGRG1 |
| Deficit biotinidaze | BTD |
| Gracil sindrom/BCS1L-poremećaji (uključujući manjak mitohondrijalnog kompleksa III, Bjornstad sindrom, Leigh sindrom) | BCS1L |
| Bloom sindrom | BLM |
| Deficit Butirlholinesteraze | BCHE |
| Canavanova bolest | ASPA |
| Deficit karbamoil-fosfatne sintaze I | CPS1 |
| Deficit karnitin-palmitoil-transferaze I | CPT1A |
| Deficit karnitin-palmitoil-transferaze II | CPT2 |
| Deficijencija Karnitin-acilkarnitin translokaze | SLC25A20 |
| Carpenter sindrom | RAB23 |
| Kateholaminergična polimorfna ventrikularna tahikardija, CASQ2- vezano | CASQ2 |
| Kateholaminergična polimorfna ventrikularna tahikardija, TRDN- vezano | TRDN |
| Cerebrotendinozna ksantomatoza | CYP27A1 |
| Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest, GDAP1-vezano | GDAP1 |
| Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest, SH3TC2-vezano | SH3TC2 |
| Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest, SURF1-vezano | SURF1 |
| Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest, tip 4B1 | MTMR2 |
| Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest, tip 4D | NDRG1 |
| Charcot-Marie-Tooth bolest, X-vezana tip 1 | GJB1 |
| Chediak-Higashi sindrom | LYST |
| Retka dečija retinalna distrofija, AIPL1-vezano | AIPL1 |
| Hondrodisplazija punktata tip 1, X-vezano | ARSE |
| Horeoakantocitoza | VPS13A |
| Horoideremija | CHM |
| Hronična granulomatozna bolest | CYBA |
| Hronična granulomatozna bolest, X-vezano | CYBB |
| Deficit citrina | SLC25A13 |
| Citrulinemija | ASS1 |
| Cockain sindrom tip A | ERCC8 |
| Cockain sindrom tip B; De Santis-Cachion sindrom | ERCC6 |
| Cohen sindrom | VPS13B |
| Kombinovana malonska i metilmalonska acidurija (ACSF3-vezana) | ACSF3 |
| Deficijencija kombinovane oksidativne fosforilacije (GFM1-vezana) | GFM1 |
| Kombinovana deficijencija oksidativne fosforilacije (TSFM-vezana) | TSFM |
| Kombinovana deficijencija hormona rasta 2 | PROP1 |
| Kombinovana deficijencija hormona rasta 3 | LHX3 |
| Kongenitalna adrenalna hiperplazija sa deficitom 11-beta-hidroksilaze | CYP11B1 |
| Kongenitalna adrenalna hiperplazija sa deficitom 17-alfa-hidrroksilaze | CYP17A1 |
| Kongenitalna adrenalna hiperplazija sa deficitom 21-hidroksilaze | CYP21A2 |
| Kongenitalna hiperplazija sa deficitom 3-beta-hidroksisteroida | HSD3B2 |
| Kongenitalna adrenalna hiperplazija, x vezana | NR0B1 |
| Kongenitalna amegakariocitna trombocitopenija | MPL |
| Kongenitalni poremećaj glikozilacije tip 1a | PMM2 |
| Kongenitalni poremećaj glikozilacije tip 1b | MPI |
| Kongenitalni poremećaj glikozilacije tip 1c | ALG6 |
| Kongenitalni hidrocefalus 1 | CCDC88C |
| Kongenitalni hiperinsulinizam; Trajni neonatalni diabetes melitus | KCNJ11 |
| Kongenitalni hipotiroidizam, povezan sa TSHB | TSHB |
| Kongenitalna ihtioza | TGM1 |
| Kongenitalna neosetljivost na bol sa anhidrozom | NTRK1 |
| Kongenitalni miastenični sindrom, povezan sa CHRNE | CHRNE |
| Kongenitalni miastenični sindrom, povezan sa RAPSN; Sekvenca deformacije fetalne akinezije | RAPSN |
| Kongenitalni nefrotski sindrom tip 1 | NPHS1 |
| Kongenitalni nefrotski sindrom tip 2 | NPHS2 |
| Kongenitalna sekretorna hloridna dijareja | SLC26A3 |
| Kongenitalni hipotireoidizam, povezan sa DUOX2 | DUOX2 |
| Kongenitalni hipotireoidizam, povezan sa DUOXA2 | DUOXA2 |
| Endotelna distrofija rožnjače | SLC4A11 |
| Nedostatak kortikosteron metiloksidaze | CYP11B2 |
| Kostefov sindrom | OPA3 |
| Sindrom deficita kreatina | SLC6A8 |
| Krigler-Najarov sindrom | UGT1A1 |
| Cistična fibroza | CFTR |
| Cistinoza | CTNS |
| Deficit D-bifunkcionalnog proteina | HSD17B4 |
| Bolest zuba 2; Loweov sindrom | OCRL |
| Deficit dihidrolipoamid dehidrogenaze | DLD |
| Deficit dihidropirimidin dehidrogenaze | DPYD |
| Donnai-Barov sindrom | LRP2 |
| Dišenova mišićna distrofija | DMD |
| Kongenitalna diskeratoza tip 5 | RTEL1 |
| Bulozna distrofična epidermoliza | COL7A1 |
| Ehler-Danlosov sindrom sa kifoskoliozom, povezan sa PLOD1 | PLOD1 |
| Ehler-Danlosov sindrom, autozomno recesivan, sa deficijencijom tenascina X | TNXB |
| Ehler-Danlosov sindrom, dermatosparaksis tip VIIC | ADAMTS2 |
| Elis van Kreveldov sindrom; povezan sa EVC; Vejersova akrofacijalna disostroza | EVC |
| Elis van Kreveldov sindrom; povezan sa EVC2; Vejersova akrodentalna disostroza | EVC2 |
| Emeri-Drajfusova mišićna distrofija | EMD |
| Sindrom pojačanog S konusa | NR2E3 |
| Etilmalonska encefalopatija | ETHE1 |
| Fabrijeva bolest | GLA |
| Deficit faktora V | F5 |
| Deficit faktora XI | F11 |
| Porodična disautonomija | ELP1 (IKBKAP) |
| Porodična hiperholesterolemija | LDLRAP1 |
| Pordični hiperinsulinizam, povezan sa ABCC8 | ABCC8 |
| Porodični deficit lipoprotein-lipaze | LPL |
| Porodična mediteranska groznica | MEFV |
| Fankonijeva anemija grupa A | FANCA |
| Fankonijeva anemija grupa C | FANCC |
| Fankonijeva anemija grupa G | FANCG |
| Fragilni X sindrom | FMR1 |
| Fraserov sindrom | GRIP1 |
| Fridrihova ataksija | FXN |
| Deficit fumaraze | FH |
| Deficit galaktokinaze | GALK1 |
| Deficit galakto-epimeraze | GALE |
| Galaktozemija | GALT |
| Gaučerova bolest | GBA |
| Gitelmanov sindrom | SLC12A3 |
| Deficit glukoza-6-fosfat dehidrogenaze | G6PD |
| Deficit glutamat formiminotransferaze | FTCD |
| Glutarna acidurija IIA | ETFA |
| Glutarna acidurija IIB | ETFB |
| Glutarna acidurija IIC | ETFDH |
| Glutarna acidurija, tip 1 | GCDH |
| Glicinska encefalopatija, povezana sa AMT | AMT |
| Glicinska encefalopatija, povezana sa GLDC | GLDC |
| Bolest skladištenja glikogena IV | GBE1 |
| Bolest skladištenja glikogena tip III | AGL |
| Bolest skladištenja glikogena tip V | PYGM |
| Bolest skladištenja glikogena VII | PFKM |
| Bolest skladištenja glikogena, tip 1a | G6PC |
| Bolest skladištenja glikogena, tip 1b | SLC37A4 |
| Deficit gvanidinoacetat metiltransferaze | GAMT |
| Giratna atrofija horoide i retine | OAT |
| Hartnupova bolest | SLC6A19 |
| Hemohromatoza, povezana sa HFE | HFE |
| Hemohromatoza, tip 2A | HJV (HFE2) |
| Hemohromatoza, tip 3 | TFR2 |
| Hemofagocitna limfohistiocistoza, porodična, 2 | PRF1 |
| Hemofilija A | F8 |
| Hemofilija B | F9 |
| Sindrom iscrpljivanja hepatocerebralne mitohondrijalne DNA, povezan sa MPV17 | MPV17 |
| Nasledna malapsorpcija folata | SLC46A1 |
| Nasledna intolerancija na fruktozu | ALDOB |
| Hermansky-Pudlakov sinrom 1 | HPS1 |
| Hermansky-Pudlakov sinrom 3 | HPS3 |
| Nedostatak holokarboksilaze sintetaze | HLCS |
| Homocistinurija (CBS-vezano) | CBS |
| Homocistinurija, kobalamin tip E | MTRR |
| Homocistinurija usled nedostatka MTHFR | MTHFR |
| Hidrolethaus sindrom tip 1 | HYLS1 |
| Hiper IgM sindrom, X-vezano | CD40LG |
| Hperimunoglobulinemija D sindrom | MVK |
| Hipermetioninemija usled deficita adenozin kinaze | ADK |
| Hipermetioninemija usled deficita S-adenosilhomocistein hidrolaze | AHCY |
| Hiperornitinemija-hiperammonemija-homocitrullinurija (HHH) sindrom | SLC25A15 |
| Hiperprolinemija tip II | ALDH4A1 |
| Hipogonadotropni hipogonadizam, GNRHR-vezano | GNRHR |
| Hipohidrotična ektodermalna displazija (EDA-vezano) | EDA |
| Hipofosfatazija | ALPL |
| Inkluziona telesna miopatija 2 | GNE |
| Infantilna neuroaksonala distrofija | PLA2G6 |
| Izovalerična acidemija | IVD |
| TMEM216-vezani poremećaji (uključujući Joubert sindrom 2 i Meckel sindrome2) | TMEM216 |
| Poremećaji udruženi sa MKS1 | MKS1 |
| Joubert sindrome 4; Senior-Løken sindrom 1; Nefronofiza | NPHP1 |
| Joubert sindrome 9; Meckel sindrom 6; COACH sindrom | CC2D2A |
| Joubert sindrom, AHI1-vezan | AHI1 |
| Joubert sindrom, ARL13B- vezan | ARL13B |
| Junkcijska (povezana) bulozna epidermoliza (LAMA3-vezano) | LAMA3 |
| Junkcijska epidermoliza buloza, LAMB3-vezano | LAMB3 |
| Junkcijska (povezana) bulozna epidermoliza (LAMC2-vezano) | LAMC2 |
| X-vezani dečiji rascep mrežnjače * | RS1 |
| Krabbe bolest | GALC |
| L1 sindrom | L1CAM |
| Leberova kongenitalna amauroza 2 | RPE65 |
| Leberova kongenitalna amauroza 5 | LCA5 |
| Leberova kongenitalna amauroza 8/povezana sa poremećajem CRB1 | CRB1 |
| Leberova kongenitalna amauroza 13 | RDH12 |
| Leighov sindrom, francusko kanadski tip | LRPPRC |
| Sindrom smrtonosne kongenitalne kontrakcije 1/smrtonosna artrogripoza sa oštećenjem neurona prednjih rogova kičmene moždine | GLE1 |
| Leukoencefalopatija sa nestajanjem bele mase (EIF2B5-vezano) | EIF2B5 |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova tip 2A (kalpainopatija) | CAPN3 |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova tip 2B (disferinopatija) | DYSF |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova tip 2C | SGCG |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova tip 2D | SGCA |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova tip 2E | SGCB |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova, tip 2F | SGCD |
| Mišićna distrofija u pojasu udova, tip 2H; Bardet-Biedl sindrom 11 | TRIM32 |
| Kongenitalna lipoidna nadbubrežna hiperplazija (STAR-vezano) | STAR |
| Lisencefalija, X-vezano | DCX |
| Prolazna dečija insuficijencija jetre (TRMU-vezano) | TRMU |
| Deficit dugog lanca 3-hidroksiacil- CoA dehidrogenaze (LCHAD); deficit trifunkcionalnog proteina | HADHA |
| Lujan-Fryns sindrom, UPF3B- vezano | UPF3B |
| Lujan-Fryns sindrom, ZDHHC9- vezano | ZDHHC9 |
| Lizinurička proteinska intolerancija | SLC7A7 |
| Intolerancija na lizinurski protein | LIPA |
| Makularna kornealna distrofija, CHST6-vezano | CHST6 |
| Bolest urina mirisa javorovog sirupa (MSUD) tip 1A | BCKDHA |
| Bolest urina mirisa javorovog sirupa (MSUD) tip 1B | BCKDHB |
| Bolest urina javorovog sirupa (MSUD) tip II | DBT |
| RPGRIP1L-vezano poremećaji (uključujući Joubert sindrom 7, COACH sindrom i Meckel sindrom 5) | RPGRIP1L |
| Deficit srednjeg lanca acil-CoA dehidrogenaze (MCAD) | ACADM |
| Megalencefalna leukoencefalopatija sa subkortikalnim cistama tipa I | MLC1 |
| Poremećaji Menkesove bolesti/povezan sa ATP7A (uključujući sindrom okcipitalnog roga i distalnu naslednu motornu neuropatiju) | ATP7A |
| MentalNA retarDACIJA, X-vezano, povezan sa fragilnim FRAXE | AFF2 |
| Metahromatska leukodistrofija (ARSA-vezano) | ARSA |
| Metahromatska leukodistrofija usled deficita sapozin-b | PSAP |
| Metilmalonska acidemija (MUT-vezano) | MUT |
| Metilmalonska acidemija sa homocistinurijom tipa kobalamin C | MMACHC |
| Metilmalonska acidemija sa homocistinurijom tipa kobalamin D | MMADHC |
| Metilmalonska acidurija sa homocistinurijom, cblF tip | LMBRD1 |
| Metilmalonska acidurija sa homocistinurijom, cblJ tip | ABCD4 |
| Metilmalonska acidemija (MMAA-vezano) | MMAA |
| Metilmalonska acidemija (MMAB-vezano) | MMAB |
| Deficit metilmalonil-CoA epimeraze | MCEE |
| Mikrocefalija, primarna autozomalo recesivna, 1 | MCPH1 |
| Mikroftalmija/klinička anoftalmija (VSX2-vezano) | VSX2 |
| Mikroftalmija, izolovana 3 | RAX |
| Nedostatak mitohondrijalnog kompleksa I / Leigh sindrom (NDUFS5-vezano) | NDUFAF5 |
| Nedostatak mitohondrijalnog kompleksa I / Leigh sindrom (NDUFS6-vezano) | NDUFS6 |
| Roberts-ov sindrom | SCO2 |
| Mitohondrijska miopatija i sideroblastična anemija 1 | PUS1 |
| Mitohondrijska neurogastrointestinalna encefalopatijska bolest (MNGIE) | TYMP |
| Mikolipidoza tip II/ III (GNPTAB-vezano) | GNPTAB |
| Mikolipidoza tip III ( GNPTG-vezano) | GNPTG |
| Mukolipidoza tip IV | MCOLN1 |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip III A (Sanfilipo A sindrom ) | SGSH |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip III D (Sanfilipo sindrom ) | GNS |
| Mukopolisaharidoza IVA (Morquio sindrom A) | GALNS |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip II (Hanterov sindrom)* | IDS |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip IIIB (Sanfilipov sindrom B) | NAGLU |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip IIIC (Sanfilipov sindrom C) | HGSNAT |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip IVB (Morkio sindrom B); GM1 - gangliozidoza | GLB1 |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip IX | HYAL1 |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip VI (Maroteo-Lamijev sindrom) | ARSB |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip VII | GUSB |
| Mukopolisaharidoza tip I (Hurlerov sindrom) | IDUA |
| Višestruki sindrom pterigijuma | CHRNG |
| Višestruki nedostatak sulfataze | SUMF1 |
| Mišićna distrofija-distroglikanopatija, FKRP-vezana | FKRP |
| Mišićna distrofija-distroglikanopatija, FKTN-vezana; Kongenitalna mišićna distrofija, Fukuyama tip | FKTN |
| Mišićna distrofija-distroglikanopatija, POMT1-vezana | POMT1 |
| Mišićna distrofija-distroglikanopatija, POMT2-vezana | POMT2 |
| Mišićna distrofija-distroglikanopatija; Retinis pigmentosa 76 | POMGNT1 |
| Mišićna distrofija, LAMA2-vezana | LAMA2 |
| Kongenitalna miotonija, autozomno dominantna; Kongenitalna miotonija, autozomno recesivna, Blaga miotonija | CLCN1 |
| Miotubularna miopatija, X-vezana | MTM1 |
| Nedostatak N-acetilglutamat sintaze | NAGS |
| Nemalinska miopatija | NEB |
| Nefrogeni dijabetes insipidus | AQP2 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, CLN3-vezana | CLN3 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, CLN5-vezana | CLN5 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, CLN6-vezana | CLN6 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, CLN8-vezana | CLN8 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, MFSD8-vezana | MFSD8 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, PPT1-vezana | PPT1 |
| Neuronska ceroidna lipofuscinoza, TPP1-vezana | TPP1 |
| Neimann-Pick-ova bolest, tip A/B | SMPD1 |
| Neimann-Pick-ova bolest, tip C1 | NPC1 |
| Neimann-Pick-ova bolest, tip C2 | NPC2 |
| Nijmegen-ov sindrom nestabilnosti | NBN |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, MYO7A-vezan; Usherov sindrom, tip 1B | MYO7A |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, PCDH15-vezan; Usherov sindrom, tip 1F | PCDH15 |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, USH1C-vezan; Usherov sindrom, tip 1C | USH1C |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, GJB2-vezan | GJB2 |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, GJB6-vezan | GJB6 |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, LOXHD1-vezan | LOXHD1 |
| Nesindromski gubitak sluha, OTOF-vezan | OTOF |
| Norijeva bolest | NDP |
| Omenov sindrom, RAG1-vezan | RAG1 |
| Omenov sindrom, RAG2-vezan | RAG2 |
| Opitz GBBB sindrom, tip 1 | MID1 |
| Nedostatak ornitin transkarbamilaze | OTC |
| Bolest krhkih kostiju, tip VIII | P3H1 |
| Osteopetroza, TCIRG1-vezana | TCIRG1 |
| Neurodegeneracija povezana sa pantotenat kinazom | PANK2 |
| Pendredov sindrom | SLC26A4 |
| Nedostatak peroksizomalne acil-CoA oksidaze | ACOX1 |
| Nedostatak fenilalanin hidroksilaze (fenilketonurija) | PAH |
| Nedostatak fosfoglicerat dehidrogenaze | PHGDH |
| Nedostatak fosfoglicerat kinaze 1 | PGK1 |
| Policistička bolest bubrega, PKHD1-vezana | PKHD1 |
| Pompeova bolest | GAA |
| Pontocerebelarna hipoplazija tip 1A | VRK1 |
| Pontocerebelarna hipoplazija tip 1B | EXOSC3 |
| Pontocerebelarna hipoplazija tip 6 | RARS2 |
| Pontocerebelarna hipoplazija tip 2D | SEPSECS |
| Postnatalna progresivna mikrocefalija sa napadima i atrofijom mozga | MED17 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, DNAH5-vezana | DNAH5 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, DNAI1-vezana | DNAI1 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, DNAI2-vezana | DNAI2 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, DNAL1-vezana | DNAL1 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, tip 14 | CCDC39 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, tip 17 | CCDC103 |
| Primarna cilijarna diskinezija, tip 30 | CCDC151 |
| Primarni urođeni glaukom | CYP1B1 |
| Primarna hiperoksalurija tip 1 | AGXT |
| Primarna hiperoksalurija tip 2 | GRHPR |
| Primarna hiperoksalurija tip 3 | HOGA1 |
| Progresivna spoljašnja oftalmoplegija; Alpers-Hutenloherov sindrom; Spektar neuropatije ataksije; Sindrom miocerebrohepatopatije | POLG |
| Progresivna porodična intrahepatična holestaza | ABCB11 |
| Propionska acidemija, PCCA-vezana | PCCA |
| Propionska acidemija, PCCB-vezana | PCCB |
| Stanja vezana za protrombin | F2 |
| Piknodizostoza | CTSK |
| Nedostatak piruvat karboksilaze | PC |
| Nedostatak piruvat dehidrogenaze E1-alfa | PDHA1 |
| Nedostatak piruvat dehidrogenaze E1-beta | PDHB |
| Bubrežna tubularna acidoza sa gluvoćom | ATP6V1B1 |
| Renpenning sindrom | PQBP1 |
| Retinitis pigmentosa 25 | EYS |
| Retinitis pigmentosa 26 | CERKL |
| Retinitis pigmentosa 28 | FAM161A |
| Retinitis pigmentosa 59 | DHDDS |
| Retinitis pigmentosa, CNGA1-vezana | CNGA1 |
| Retinitis pigmentosa, CNGB1-vezana | CNGB1 |
| Retinitis pigmentosa, IDH3B-vezana | IDH3B |
| Retinitis pigmentoza, PDE6A-vezana | PDE6A |
| Rizomelična hondroplazija punktata, tip 1 | PEX7 |
| Rizomelična hondroplazija punktata, tip 3 | AGPS |
| Robertsonov sindrom | ESCO2 |
| Sandhoffa bolest | HEXB |
| Šimkeova imunokoštana displazija | SMARCAL1 |
| Šindlerova bolest tip I; Šindlerova bolest tip III | NAGA |
| Schopf-Schulz-Passarge sindrom; Odontoonihodermalna displazija | WNT10A |
| Segawa sindrom | TH |
| Teška kombinovana imunodeficijencija sa osetljivošću na jonizujuće zračenje | DCLRE1C |
| Teška kombinovana imunodeficijencija, JAK3-vezana | JAK3 |
| Teška kombinovana imunodeficijencija, X-vezana | IL2RG |
| Teška kongenitalna neutropenija, HAX1-vezana | HAX1 |
| Teška kongenitalna neutropenija, VPS45-vezana | VPS45 |
| Deficit kratkog lanca acil-CoA dehidrogenaze (SBCAD) | ACADSB |
| Deficit kratkog lanca acil-CoA dehidrogenaze (SCAD) | ACADS |
| Displazija 3 kratkih rebara toraksa sa ili bez polidaktilije | DYNC2H1 |
| Poremećaj skladištenja sijalinske kiseline | SLC17A5 |
| Anemija srpastih ćelija; Beta talasemija | HBB |
| Sjögren-Larsson sindrom | ALDH3A2 |
| Smith-Lemli-Opitz sindrom | DHCR7 |
| Spastična paraplegija 15 | ZFYVE26 |
| Spastična paraplegija 2, X-vezano (SPG2) | PLP1 |
| Spastična paraplegija 49 | TECPR2 |
| Spastična paraplegija tip 7 | SPG7 |
| SPG11-vezan neuromišićni poremećaj | SPG11 |
| Spinalna mišićna atrofija | SMN1 |
| Spinocerebelarna ataksija, autozomalno recesivna 10 | ANO10 |
| Spondilokostalna disostoza | MESP2 |
| Steel sindrom | COL27A1 |
| Stuve-Wiedemann sindrom | LIFR |
| Pulmonarna disfunkcija metabolizma surfaktanata; Intestinalna bolest pluća | ABCA3 |
| Sistemski primarni deficit karnitina | SLC22A5 |
| Tay-Sachs-ova bolest | HEXA |
| Deficit tetrahidrobiopterina | PTS |
| Deficit tetrahidrobiopterina, PCBD1-vezan | PCBD1 |
| Deficit tetrahidrobiopterina, QDPR-vezan | QDPR |
| Sindrom disfunkcije metabolizma tiamina 2 (biotin ili tiamin odgovoran) | SLC19A3 |
| Dyshormonogenesis štitne žlezde, IYD-vezan | IYD |
| Dyshormonogenesis štitne žlezde, SLC5A5-vezan | SLC5A5 |
| Dyshormonogenesis štitne žlezde, TG-vezan | TG |
| Dyshormonogenesis štitne žlezde, TPO-vezan | TPO |
| Treacher Collins sindrom, POLR1C-vezan | POLR1C |
| Trihohetatoenterični sindrom | TTC37 |
| Trihotiodistrofija 1, fotosenzitivna; Xeroderma pigmentoza, grupa D | ERCC2 |
| Trimetilaminurija | FMO3 |
| Tirozinemija, tip 1 | FAH |
| Tirozinemija, tip II | TAT |
| Usher sindrom tip 2D | WHRN |
| Usher sindrom tip 1G | USH1G |
| Ušer sindrom tip 1D | CDH23 |
| Usher sindrom tip 2A | USH2A |
| Usher sindrom tip 3A | CLRN1 |
| Deficit jako dugog lanca acil-CoA dehidrogenaze (VLCAD) | ACADVL |
| Vitamin D zavisni rahitis, tip 1A | CYP27B1 |
| Wilsonova bolest | ATP7B |
| Wiskot-Aldrich sindrom, X-vezana trombocitopenija, teška kongenitalna neutropenija, WAS-vezana | WAS |
| Wolcott-Raillson sindrom | EIF2AK3 |
| X-vezan Aarskog-Scott sindrom | FGD1 |
| X-vezana epilepsija sa varijabilnim poteškoćama u učenju | SYN1 |
| X-vezan gubitak sluha, POU3F4-vezan | POU3F4 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće sa hipoplazijom malog mozga i karakterističnim izgledom lica | OPHN1 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, AP1S2-vezane | AP1S2 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, ARX-vezane | ARX |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, BRWD3-vezane | BRWD3 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, CUL4B-vezane | CUL4B |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, DLG3-vezane | DLG3 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, FTSJ1-vezane | FTSJ1 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, IL1RAPL1-vezane | IL1RAPL1 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, KDM5C-vezane | KDM5C |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, PAK3-vezane | PAK3 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, PHF8-vezane | PHF8 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, THOC2-vezane | THOC2 |
| X-vezane intelektualne poteškoće, ZNF711-vezane | ZNF711 |
| X-vezani albinizam oka, GPR143-vezan | GPR143 |
| X-vezana retinitis pigmentoza, RP2-vezana | RP2 |
| X-vezana retinitis pigmentoza, RPGR-vezana | RPGR |
| Kseroderma pigmentoza, grupa A | XPA |
| Kseroderma pigmentoza, grupa C | XPC |
| Zellweger-ov sindrom, PEX1-vezan | PEX1 |
| Zellweger-ov sindrom, PEX10-vezan | PEX10 |
| Zellweger-ov sindrom, PEX12-vezan | PEX12 |
| Zellweger-ov sindrom, PEX2-vezan | PEX2 |
| Zellweger-ov sindrom, PEX6-vezan | PEX6 |
Spisak bolesti koje analizira

COMPLETE
| AAAS | Triple-A syndrome (achalasia-addisonianism-alacrimia) |
| AARS1 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 29 |
| AARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 8; Leukoencephalopathy, progressive, with ovarian failure |
| AASS | Hyperlysinemia, type 1 and type 2 |
| ABAT | GABA-transaminase deficiency |
| ABCA1 | Tangier disease |
| ABCA12 | Ichthyosis congenital autosomal recessive type 4A and 4B (harlequin) |
| ABCA3 | Surfactant metabolism dysfunction, pulmonary, type 3 |
| ABCA4 | Stargardt disease type 1; Cone-rod dystrophy type 3 |
| ABCB11 | Cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic, type 2; Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, type 2 |
| ABCB4 | Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, type 3 |
| ABCB7 | Anemia, sideroblastic, with ataxia |
| ABCC2 | Dubin-Johnson syndrome |
| ABCC6 | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum; Generalized arterial calcification of infancy, type 2 |
| ABCC8 | Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, type 1 (congenital hyperinsulinism); Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) |
| ABCD1 | Adrenoleukodystrophy |
| ABCD4 | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblJ type |
| ABCG5 | Sitosterolemia |
| ABCG8 | Sitosterolemia |
| ABHD12 | PHARC syndrome (polyneuropathy, hearing loss, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa and cataract) |
| ABHD5 | Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome |
| ACAD8 | Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ACAD9 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase 9 deficiency (mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear, type 20) |
| ACADM | Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ACADS | Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ACADSB | Short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (2-methylbuyrylglycinuria) |
| ACADVL | Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficiency |
| ACAT1 | Alpha-methylacetoacetic aciduria (3-ketothiolase deficiency) |
| ACE | Renal tubular dysgenesis |
| ACO2 | Infantile cerebellar-retinal degeneration |
| ACOX1 | Peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase deficiency |
| ACOX2 | Bile acid synthesis defect, congenital, type 6 |
| ACP5 | Spondyloenchondrodysplasia with immune dysregulation |
| ACSF3 | Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria |
| ACSL4 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 63 |
| ACTA1 | Nemaline myopathy 3; Congenital fiber-type disproportion myopathy 1 |
| ACTN4 | Glomerulosclerosis, focal segmental, 1 |
| ACY1 | Aminoacylase 1 deficiency |
| ADA | Severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA) |
| ADA2 | Vasculitis, autoinflammation, immunodeficiency, and hematologic defects syndrome |
| ADAM9 | Cone-rod dystrophy 9 |
| ADAMTS10 | Weill-Marchesani syndrome, type 1 recessive |
| ADAMTS13 | Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, familial (Schulman-Upshaw syndrome) |
| ADAMTS17 | Weill-Marchesani syndrome, type 4 recessive |
| ADAMTS18 | Microcornea, myopic chorioretinal atrophy, and telecanthus |
| ADAMTS2 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, dermatosparaxis type |
| ADAMTSL2 | Geleophysic dysplasia type 1 |
| ADAMTSL4 | Ectopia lentis et pupillae; Ectopia lentis, isolated, type 2 |
| ADAR | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 6 |
| ADAT3 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with brain abnormalities, poor growth, and dysmorphic facies |
| ADCK3 | Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, 4 |
| ADGRG1 | Polymicrogyria, bilateral frontoparietal |
| ADGRG6 | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 9 |
| ADGRV1 | Usher syndrome, type 2C |
| ADK | Hypermethioninemia due to adenosine kinase deficiency |
| ADSL | Adenylosuccinase deficiency |
| ADSS1 | Myopathy, distal, 5 |
| AFF2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 109 |
| AFG3L2 | Spastic ataxia, type 5 autosomal recessive |
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein deficiency |
| AGA | Aspartylglucosaminuria (glycosylasparaginase deficiency) |
| AGBL5 | Retinitis pigmentosa 75 |
| AGK | Cataract 38; Sengers syndrome |
| AGL | Glycogen storage disease, type 3 |
| AGPAT2 | Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (Berardinelli-Seip syndrome) |
| AGPS | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 3 |
| AGRN | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 8 |
| AGT | Renal tubular dysgenesis |
| AGTR1 | Renal tubular dysgenesis |
| AGXT | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 1 |
| AHCY | Hypermethioninemia with deficiency of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase |
| AHI1 | Joubert syndrome, type 3 |
| AICDA | Immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM, type 2 |
| AIMP1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 3 |
| AIMP2 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 17 |
| AIPL1 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 4 |
| AIRE | Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome, type 1 |
| AK1 | Hemolytic anemia due to adenylate kinase deficiency |
| AK2 | Reticular dysgenesis |
| AKR1C2 | 46,XY disorder of sex development due to testicular 17,20-desmolase deficiency |
| AKR1D1 | Bile acid synthesis defect, congenital, type 2 |
| ALAD | Porphyria, acute hepatic |
| ALAS2 | Anemia, sideroblastic, 1 |
| ALB | Analbuminemia |
| ALDH18A1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 9B, autosomal recessive; Cutis laxa, type 3A (De Barsy syndrome) |
| ALDH1A3 | Microphthalmia, isolated 8 |
| ALDH3A2 | Sjogren-Larsson syndrome |
| ALDH4A1 | Hyperprolinemia, type 2 |
| ALDH5A1 | Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ALDH6A1 | Methylmalonate semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ALDH7A1 | Epilepsy, pyridoxine-dependent |
| ALDOA | Glycogen storage disease type 12 |
| ALDOB | Fructose intolerance, hereditary |
| ALG1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1K |
| ALG11 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1P |
| ALG12 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1G |
| ALG2 | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 14 with tubular aggregates |
| ALG3 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1D |
| ALG6 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1C |
| ALG8 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1H |
| ALG9 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1L; Gillessen-Kaesbach-Nishimura syndrome |
| ALMS1 | Alström syndrome |
| ALOX12B | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| ALOXE3 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 3 |
| ALPK3 | Cardiomyopathy, familial hypertrophic, type 27 |
| ALPL | Hypophosphatasia, infantile/childhood |
| ALS2 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, type 2 juvenile; Primary lateral sclerosis, juvenile; Spastic paralysis, infantile onset ascending |
| ALX1 | Frontonasal dysplasia, type 3 |
| ALX3 | Frontonasal dysplasia, type 1 |
| ALX4 | Frontonasal dysplasia, type 2 |
| AMACR | Bile acid synthesis defect, congenital, type 4; Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase deficiency |
| AMBN | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type IF |
| AMH | Persistent Mullerian duct syndrome, type 1 |
| AMHR2 | Persistent Mullerian duct syndrome, type II |
| AMN | Megaloblastic anemia 1 (Imerslund-Grasbeck syndrome) |
| AMPD1 | Myopathy due to myoadenylate deaminase deficiency |
| AMPD2 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 9 |
| AMT | Glycine encephalopathy |
| ANGPTL3 | Hypobetalipoproteinemia, familial, type 2 |
| ANKS6 | Nephronophthisis 16 |
| ANO10 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 10 |
| ANO5 | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 12 (LGMD R12) |
| ANTXR1 | GAPO syndrome |
| ANTXR2 | Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome |
| AP1S1 | MEDNIK syndrome |
| AP1S2 | Pettigrew syndrome |
| AP3B1 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 2 |
| AP3B2 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 48 |
| AP3D1 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 10 |
| AP4B1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 47 autosomal recessive |
| AP4E1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 51 autosomal recessive |
| AP4M1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 50 autosomal recessive |
| AP4S1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 52 autosomal recessive |
| AP5Z1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 48 autosomal recessive |
| APOC2 | Hyperlipoproteinemia, type 1B |
| APOE | Sea-blue histiocyte disease |
| APRT | Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency |
| APTX | Ataxia, early-onset, with oculomotor apraxia and hypoalbuminemia |
| AQP2 | Diabetes insipidus, nephrogenic, type 2 |
| AR | Androgen insensitivity syndrome, complete |
| ARFGEF2 | Periventricular heterotopia with microcephaly |
| ARG1 | Argininemia (arginase deficiency) |
| ARHGDIA | Nephrotic syndrome, type 8 |
| ARHGEF18 | Retinitis pigmentosa 78 |
| ARHGEF9 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 8 |
| ARL13B | Joubert syndrome type 8 |
| ARL2BP | Retinitis pigmentosa with or without situs inversus |
| ARL6 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 3 |
| ARMC9 | Joubert syndrome 30 |
| ARPC1B | Immunodeficiency, type 71 with inflammatory disease and congenita thrombocytopenia |
| ARSA | Metachromatic leukodystrophy |
| ARSB | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 6 (Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome) |
| ARSE | Chondrodysplasia punctata, X-linked recessive |
| ARSL | Chondrodysplasia punctata, brachytelephalangic |
| ARV1 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 38 |
| ARX | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 1; ARX-related developmental disorders |
| ASAH1 | Farber lipogranulomatosis; Spinal muscular atrophy with progressive myoclonic epilepsy |
| ASL | Argininosuccinic aciduria |
| ASNS | Asparagine synthetase deficiency |
| ASPA | Canavan disease |
| ASPH | Traboulsi syndrome |
| ASPM | Primary microcephaly type 5 autosomal recessive |
| ASS1 | Citrullinemia, type 1 |
| ATAD1 | Hyperekplexia 4 |
| ATF6 | Achromatopsia, type 7 |
| ATIC | AICA-ribosiduria due to ATIC deficiency |
| ATM | Ataxia-telangiectasia |
| ATOH7 | Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous, autosomal recessive |
| ATP13A2 | Kufor-Rakeb syndrome; Spastic paraplegia, type 78 autosomal recessive |
| ATP2A1 | Brody myopathy |
| ATP6AP2 | Parkinsonism with spasticity, X-linked |
| ATP6V0A2 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 2A; Wrinkly skin syndrome |
| ATP6V0A4 | Renal tubular acidosis, distal, autosomal recessive |
| ATP6V1A | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 2D |
| ATP6V1B1 | Renal tubular acidosis with deafness |
| ATP6V1E1 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 2C |
| ATP7A | Menkes disease; Occipital horn syndrome |
| ATP7B | Wilson disease |
| ATP8B1 | Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, type 1; Cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic, type 1 |
| ATR | Seckel syndrome, type 1 |
| ATRX | Intellectual disability-hypotonic facies syndrome, X-linked; Alpha-thalassemia/intellectual developmental disorder syndrome |
| AUH | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 1 |
| AURKC | Spermatogenic failure, type 5 |
| AVIL | Nephrotic syndrome, type 21 |
| AVPR2 | Diabetes insipidus, nephrogenic, 1; Nephrogenic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis |
| B2M | Immunodeficiency, type 43 |
| B3GALNT2 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies, type A, 11 |
| B3GALT6 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, spondylodysplastic type, 2 |
| B3GAT3 | Multiple joint dislocations, short stature, craniofacial dysmorphism, with or without congenital heart defects |
| B3GLCT | Peters-plus syndrome |
| B4GALNT1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 26 autosomal recessive |
| B4GALT1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2D |
| B4GALT7 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, spondylodysplastic, type 1 |
| B4GAT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A, 13 |
| B9D1 | Joubert syndrome, type 27; ?Meckel syndrome 9 |
| B9D2 | Joubert syndrome, type 34; ?Meckel syndrome, type 10 |
| BBS1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 1 |
| BBS10 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 10 |
| BBS12 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 12 |
| BBS2 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 2 |
| BBS4 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 4 |
| BBS5 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 5 |
| BBS7 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 7 |
| BBS9 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 9 |
| BCAT2 | Hypervalinemia or hyperleucine-isoleucinemia |
| BCHE | Butyrylcholinesterase deficiency |
| BCKDHA | Maple syrup urine disease, type 1A |
| BCKDHB | Maple syrup urine disease, type 1B |
| BCKDK | Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase deficiency |
| BCL10 | Immunodeficiency, type 37 |
| BCOR | Microphthalmia, syndromic 2 |
| BCS1L | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency nuclear type 1; GRACILE syndrome; Bjornstad syndrome |
| BEST1 | Bestrophinopathy, AR |
| BFSP1 | Cataract 33 multiple types |
| BHLHA9 | Syndactyly, mesoaxial synostotic, with phalangeal reduction |
| BIN1 | Centronuclear myopathy, type 2 |
| BLM | Bloom syndrome |
| BLNK | Agammaglobulinemia 4 |
| BLOC1S3 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 8 |
| BLOC1S6 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 9 |
| BLVRA | Hyperbiliverdinemia |
| BMP1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 13 |
| BMPER | Diaphanospondylodysostosis |
| BMPR1B | Acromesomelic dysplasia, Demirhan type |
| BOLA3 | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 2 with hyperglycinemia |
| BPGM | Erythrocytosis due to bisphosphoglycerate mutase deficiency |
| BPNT2 | Chondrodysplasia with joint dislocations, GPAPP type |
| BRAT1 | Rigidity and multifocal seizure syndrome, lethal neonatal; Neurodevelopmental disorder with cerebellar atrophy and with or without seizures |
| BRCA2 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group D1 |
| BRF1 | Cerebellofaciodental syndrome |
| BRIP1 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group J |
| BRWD3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 93 |
| BSCL2 | Congenital generalized lipodystrophy, type 2; Encephalopathy, progressive, with or without lipodystrophy |
| BSND | Bartter syndrome, type 4A |
| BTD | Biotinidase deficiency |
| BTK | Agammaglobulinemia X-linked, type 1 |
| BUB1B | Mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome 1 |
| C10orf2 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 7 (hepatocerebral type) |
| C12orf57 | Temtamy syndrome |
| C12orf65 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency, type 7; Spastic paraplegia, type 55, autosomal recessive |
| C19orf12 | Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation, type 4 |
| C1QA | C1q deficiency |
| C1QB | C1q deficiency |
| C1QBP | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 |
| C1QC | C1q deficiency |
| C1S | C1s deficiency |
| C2 | C2 deficiency |
| C2CD3 | Orofaciodigital syndrome, type 14 |
| C3 | Complement component 3 deficiency |
| C5 | Complement component 5 deficiency |
| C6 | Complement component 6 deficiency |
| C7 | Complement component 7 deficiency |
| C8B | Complement component 8 deficiency, type 2 |
| C8orf37 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type21 |
| CA12 | Hyperchlorhidrosis, isolated |
| CA2 | Osteopetrosis with renal tubular acidosis (osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive, type 3) |
| CA5A | Hyperammonemia due to carbonic anhydrase VA deficiency |
| CA8 | Cerebellar ataxia, impaired intellectual development and dysequilibrium syndrome 3 |
| CABP2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 93 |
| CABP4 | Congenital stationary night blindness, type 2B |
| CACNA1D | Sinoatrial node dysfunction and deafness |
| CACNA2D4 | Retinal cone dystrophy 4 |
| CAD | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 50 |
| CALCRL | Lymphatic malformation 8 |
| CANT1 | Desbuquois dysplasia, type 1; Epiphyseal dysplasia, multiple, type 7 |
| CAPN1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 76 autosomal recessive |
| CAPN3 | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 1 (LGMD R1) |
| CARD11 | Immunodeficiency, type 11A |
| CARD9 | Candidiasis, familial, type 2 autosomal recessive |
| CARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 27 |
| CASK | FG syndrome 4 |
| CASP14 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 12 |
| CASQ2 | Ventricular tachycardia, catecholaminergic polymorphic, type 2 |
| CASR | Hyperparathyroidism, neonatal |
| CAST | Peeling skin with leukonychia, acral punctate keratoses, cheilitis, and knuckle pads |
| CAT | Acatalasemia |
| CATSPER1 | Spermatogenic failure, type 7 |
| CAVIN1 | Lipodystrophy, congenital generalized, type 4 |
| CBLIF | Intrinsic factor deficiency |
| CBS | Homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase |
| CC2D1A | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 3 |
| CC2D2A | Joubert syndrome, type 9; Meckel syndrome, type 6; COACH syndrome, 2 |
| CCBE1 | Hennekam lymphangiectasia-lymphedema syndrome, type 1 |
| CCDC103 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 17 |
| CCDC115 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type IIo |
| CCDC174 | Hypotonia, infantile, with psychomotor retardation |
| CCDC39 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 14 |
| CCDC40 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 15 |
| CCDC65 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 27 |
| CCDC8 | 3M syndrome 3 |
| CCDC88C | Hydrocephalus, congenital, type 1 |
| CCN6 | Arthropathy, progressive pseudorheumatoid, of childhood |
| CCNO | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 29 |
| CD19 | Immunodeficiency, common variable, type 3 |
| CD247 | Immunodeficiency, type 25 |
| CD27 | Lymphoproliferative syndrome 2 |
| CD2AP | Glomerulosclerosis, focal segmental, type 3 susceptibility to |
| CD320 | Methylmalonic aciduria, transient, due to transcobalamin receptor defect |
| CD36 | Platelet glycoprotein 4 deficiency |
| CD3D | Immunodeficiency, type 19 |
| CD3E | Immunodeficiency, type 18 |
| CD3G | Immunodeficiency, type 17 CD3 gamma deficient |
| CD40 | Immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM, type 3 |
| CD40LG | Hyper-IgM syndrome, type 1 (immunodeficiency, X-linked, with hyper-IgM, type 1) |
| CD55 | Complement hyperactivation, angiopathic thrombosis, and protein-losing enteropathy (CHAPLE) |
| CD59 | CD59 deficiency |
| CD79A | Agammaglobulinemia 3 |
| CD79B | Agammaglobulinemia 6 |
| CD81 | Immunodeficiency, common variable, type 6 |
| CD8A | CD8 deficiency, familial |
| CDAN1 | Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital, type 1A |
| CDC14A | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 105 |
| CDC45 | Meier-Gorlin syndrome 7 |
| CDCA7 | Immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies syndrome 3 |
| CDH11 | Elsahy-Waters syndrome |
| CDH23 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 12; Usher syndrome, type 1D |
| CDH3 | Ectodermal dysplasia, ectrodactyly, and macular dystrophy |
| CDHR1 | Cone-rod dystrophy, type 15 |
| CDIN1 | Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital, type Ib |
| CDK10 | Al Kaissi syndrome |
| CDK5RAP2 | Primary microcephaly type 3 autosomal recessive |
| CDKL5 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 2 |
| CDSN | Peeling skin syndrome 1 |
| CDT1 | Meier-Gorlin syndrome, type 4 |
| CEBPE | Specific granule deficiency |
| CENPF | Stromme syndrome |
| CENPJ | Primary microcephaly type 6 autosomal recessive |
| CEP104 | Joubert syndrome 25 |
| CEP120 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 13 with or without polydactyly |
| CEP135 | Microcephaly 8 primary, autosomal recessive |
| CEP152 | Primary microcephaly type 9 autosomal recessive |
| CEP164 | Nephronophthisis 15 |
| CEP19 | Morbid obesity and spermatogenic failure |
| CEP290 | Meckel syndrome, type 4; Joubert syndrome, type 5; Leber congenital amaurosis, type 10 |
| CEP41 | Joubert syndrome, type 15 |
| CEP55 | Multinucleated neurons, anhydramnios, renal dysplasia, cerebellar hypoplasia, and hydranencephaly |
| CEP57 | Mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome 2 |
| CEP78 | Cone-rod dystrophy and hearing loss |
| CEP83 | Nephronophthisis 18 |
| CERKL | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 26 |
| CERS3 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 9 |
| CFAP43 | Spermatogenic failure, type 19 |
| CFAP53 | Heterotaxy, visceral, 6 autosomal recessive |
| CFD | Complement factor D deficiency |
| CFH | Complement factor H deficiency |
| CFI | Complement factor I deficiency |
| CFL2 | Nemaline myopathy, type 7 autosomal recessive |
| CFP | Properdin deficiency, X-linked |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis |
| CHAT | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 6 presynaptic |
| CHKB | Muscular dystrophy, congenital, megaconial type |
| CHM | Choroideremia |
| CHMP1A | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 8 |
| CHRNA1 | Multiple pterygium syndrome, lethal type |
| CHRNB1 | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 2C, associated with acetylcholine receptor deficiency |
| CHRND | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 3B, fast-channel; Multiple pterygium syndrome, lethal type |
| CHRNE | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 4B, fast-channel; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 4C, associated with acetylcholine receptor deficiency |
| CHRNG | Multiple pterygium syndrome (MPS), Escobar type; MPS, lethal type |
| CHST14 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, musculocontractural, type 1 |
| CHST3 | Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia with congenital joint dislocations |
| CHST6 | Macular corneal dystrophy |
| CHSY1 | Temtamy preaxial brachydactyly syndrome |
| CHUK | Cocoon syndrome |
| CIB2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 48; Usher syndrome, type 1J |
| CIITA | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 2 complementation group A |
| CILK1 | Endocrine-cerebroosteodysplasia |
| CISD2 | Wolfram syndrome 2 |
| CIT | Microcephaly 17 primary, autosomal recessive |
| CKAP2L | Filippi syndrome |
| CLCF1 | Cold-induced sweating syndrome 2 |
| CLCN1 | Myotonia congenita, recessive |
| CLCN2 | Leukoencephalopathy with ataxia |
| CLCN5 | Dent disease 1 |
| CLCN7 | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive type 4 |
| CLCNKA | Bartter syndrome, type 4B, digenic |
| CLCNKB | Bartter syndrome, type 3; Bartter syndrome, type 4B, digenic |
| CLDN1 | Ichthyosis, leukocyte vacuoles, alopecia, and sclerosing cholangitis |
| CLDN10 | HELIX syndrome |
| CLDN14 | Deafness type 29 autosomal recessive |
| CLDN16 | Hypomagnesemia, type 3 renal |
| CLDN19 | Rena hypomagnesemia type 5 with ocular involvement |
| CLMP | Congenital short bowel syndrome |
| CLN3 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 3 |
| CLN5 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 5 |
| CLN6 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 6 |
| CLN8 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 8 |
| CLP1 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 10 |
| CLPB | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 7 with cataracts, neurologic involvement and neutropenia |
| CLPP | Perrault syndrome 3 |
| CLRN1 | Usher syndrome, type 3A |
| CNGA1 | Retinitis pigmentosa type 49 |
| CNGA3 | Achromatopsia, type 2 |
| CNGB1 | Retinitis pigmentosa type 45 |
| CNGB3 | Achromatopsia, type 3 |
| CNNM2 | Hypomagnesemia, seizures, and intellectual developmental disorder |
| CNNM4 | Jalili syndrome |
| CNPY3 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 60 |
| CNTNAP1 | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 7 |
| CNTNAP2 | Pitt-Hopkins like syndrome 1 |
| COA6 | Cardioencephalomyopathy, fatal infantile, due to cytochrome c oxidase deficiency 4 |
| COA8 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 17 |
| COASY | Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 6 |
| COG1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type IIg |
| COG4 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2J |
| COG5 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2I |
| COG6 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2L; Shaheen syndrome |
| COG7 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2E |
| COG8 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2H |
| COL11A1 | Fibrochondrogenesis type 1 |
| COL11A2 | Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia, autosomal recessive |
| COL13A1 | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 19 |
| COL17A1 | Epidermolysis bullosa, junctional, non-Herlitz type |
| COL18A1 | Knobloch syndrome, type 1 |
| COL25A1 | Fibrosis of extraocular muscles, congenital, type 5 |
| COL27A1 | Steel syndrome |
| COL4A3 | Alport syndrome, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| COL4A4 | Alport syndrome, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| COL4A5 | Alport syndrome, X-linked |
| COL6A1 | Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, type 1 (Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 22 [LGMD R22]) |
| COL6A2 | Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, type 1 (Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 22 [LGMD R22]) |
| COL6A3 | Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, type 1 (Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 22 [LGMD R22]) |
| COL7A1 | Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB), Hallopeau-Siemens (HS) type and non-HS type; DEB pruriginosa; DEB pretibial |
| COL9A1 | Stickler syndrome, type 4 |
| COL9A2 | Stickler syndrome, type V |
| COLEC10 | 3MC syndrome 3 |
| COLEC11 | 3MC syndrome 2 |
| COLQ | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 5 |
| COQ2 | Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency, type 1 |
| COQ4 | Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, type 7 |
| COQ6 | Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, type 6 |
| COQ8A | Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency, type 4 |
| COQ8B | Nephrotic syndrome, type 9 |
| COQ9 | Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, type 5 |
| CORO1A | Immunodeficiency, type 8 |
| COX10 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 3 |
| COX15 | Cardioencephalomyopathy, fatal infantile, due to cytochrome c oxidase deficiency, type 2; Leigh syndrome due to cytochrome c oxidase deficiency |
| COX20 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 11 |
| COX6B1 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 7 |
| CP | Aceruloplasminemia |
| CPA6 | Febrile seizures, familial, type 11 |
| CPAMD8 | Anterior segment dysgenesis, type 8 |
| CPLANE1 | Joubert syndrome 17 |
| CPLX1 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 63 |
| CPS1 | Carbamoylphosphate synthetase 1 deficiency |
| CPT1A | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type 1A deficiency, hepatic |
| CPT2 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type 2 deficiency, lethal neonatal; Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type 2 deficiency, infantile |
| CR2 | Immunodeficiency, common variable, type 7 |
| CRADD | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 34 with variant lissencephaly |
| CRB1 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 12; Leber congenital amaurosis, type 8 |
| CRB2 | Ventriculomegaly with cystic kidney disease |
| CRBN | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| CRIPT | Short stature with microcephaly and distinctive facies |
| CRLF1 | Cold-induced sweating syndrome type 1 |
| CRPPA | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type A7; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type C7 |
| CRTAP | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 7 |
| CRYAA | Cataract 9 multiple types |
| CRYAB | Myopathy, myofibrillar, fatal infantile hypertonic, alpha-B crystallin-related; Cataract 16 multiple types |
| CRYBB1 | Cataract 17 |
| CRYBB3 | Cataract 22 |
| CSF2RB | Surfactant metabolism dysfunction, pulmonary, type 5 |
| CSF3R | Neutropenia, severe congenital, type 7 autosomal recessive |
| CSPP1 | Joubert syndrome 21 |
| CSTA | Peeling skin syndrome, type 4 |
| CSTB | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic type 1A (Unverricht and Lundborg) |
| CTC1 | Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts |
| CTH | Cystathioninuria |
| CTNS | Nephropathic cystinosis |
| CTPS1 | Immunodeficiency, type 24 |
| CTSA | Galactosialidosis |
| CTSC | Haim-Munk syndrome; Papillon-Lefevre syndrome |
| CTSD | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 10 |
| CTSF | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 13 (Kufs type) |
| CTSK | Pycnodysostosis |
| CUBN | Megaloblastic anemia 1 (Imerslund-Grasbeck syndrome) |
| CUL4B | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Cabezas type |
| CUL7 | 3M syndrome 1 |
| CWC27 | Retinitis pigmentosa with or without skeletal anomalies |
| CWF19L1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 17 |
| CYB5A | 46,XY disorder of sex development due to isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency |
| CYB5R3 | Methemoglobinemia, type 1; Methemoglobinemia, type 2 |
| CYBA | Chronic granulomatous disease, type 4 |
| CYBB | Chronic granulomatous disease, X-linked |
| CYC1 | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 6 |
| CYP11A1 | 46,XY disorder of sex development-adrenal insufficiency due to CYP11A1 deficiency |
| CYP11B1 | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency |
| CYP11B2 | Hypoaldosteronism, congenital, due to CMO I deficiency |
| CYP17A1 | 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency |
| CYP19A1 | Aromatase deficiency |
| CYP1B1 | Glaucoma, primary congenital, type 3A |
| CYP21A2 | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency |
| CYP24A1 | Hypercalcemia, infantile, type 1 |
| CYP26B1 | Craniosynostosis with radiohumeral fusions and other skeletal and craniofacial anomalies |
| CYP26C1 | Focal facial dermal dysplasia 4 |
| CYP27A1 | Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis |
| CYP27B1 | Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type 1 |
| CYP2R1 | Rickets due to defect in vitamin D 25-hydroxylation |
| CYP2U1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 56 autosomal recessive |
| CYP4F22 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 5 |
| CYP4V2 | Bietti crystalline corneoretinal dystrophy |
| CYP7B1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 5A, autosomal recessive |
| D2HGDH | D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria |
| DAG1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy type A9; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy type C9 |
| DARS1 | Hypomyelination with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and leg spasticity |
| DARS2 | Leukoencephalopathy with brain stem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation |
| DBH | Dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency |
| DBT | Maple syrup urine disease, type 2 |
| DCAF17 | Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome |
| DCC | Gaze palsy, familial horizontal, with progressive scoliosis, type 2 |
| DCDC2 | Sclerosing cholangitis, neonatal; Nephronophthisis 19 |
| DCHS1 | Van Maldergem syndrome 1 |
| DCLRE1C | Omenn syndrome; Severe combined immunodeficiency, Athabascan type |
| DCPS | Al-Raqad syndrome |
| DCX | Lissencephaly, X-linked, type 1 |
| DDB2 | Xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group E |
| DDC | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency |
| DDHD1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 28 autosomal recessive |
| DDHD2 | Spastic paraplegia, type 54 autosomal recessive |
| DDR2 | Spondylometaepiphyseal dysplasia, short limb-hand type |
| DDRGK1 | Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Shohat type |
| DDX11 | Warsaw breakage syndrome |
| DDX59 | Orofaciodigital syndrome V |
| DENND5A | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 49 |
| DES | Myopathy, myofibrillar, type 1 |
| DGAT1 | Diarrhea 7 protein-losing enteropathy type |
| DGKE | Nephrotic syndrome, type 7 |
| DGUOK | DGUOK-related mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome |
| DHCR24 | Desmosterolosis |
| DHCR7 | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome |
| DHDDS | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 59 |
| DHFR | Megaloblastic anemia due to dihydrofolate reductase deficiency |
| DHH | 46,XY complete gonadal dysgenesis |
| DHODH | Miller syndrome |
| DHPS | Neurodevelopmental disorder with seizures and speech and walking impairment |
| DHTKD1 | 2-aminoadipic 2-oxoadipic aciduria |
| DIAPH1 | Seizures, cortical blindness, microcephaly syndrome |
| DIS3L2 | Perlman syndrome |
| DKC1 | Dyskeratosis congenita, X-linked |
| DLAT | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 deficiency |
| DLD | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency |
| DLG3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 90 |
| DLL3 | Spondylocostal dysostosis type 1 |
| DMD | Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy |
| DMGDH | Dimethylglycine dehydrogenase deficiency |
| DMP1 | Hypophosphatemic rickets, autosomal recessive |
| DMXL2 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, type 81 |
| DNAAF1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 13 |
| DNAAF2 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 10 |
| DNAAF3 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 2 |
| DNAAF4 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 25 |
| DNAAF5 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 18 |
| DNAH1 | Spermatogenic failure, type 18 |
| DNAH11 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 7 with or without situs inversus |
| DNAH5 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 3 with or without situs inversus |
| DNAH9 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 40 |
| DNAI1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 1 with or without situs inversus |
| DNAI2 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 9 with or without situs inversus |
| DNAJB13 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 34 |
| DNAJB2 | Spinal muscular atrophy, distal, autosomal recessive, type 5 |
| DNAJC12 | Hyperphenylalaninemia, mild, non-BH4-deficient |
| DNAJC19 | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 5 |
| DNAJC21 | Bone marrow failure syndrome, type 3 |
| DNAJC6 | Parkinson disease, type 19A, juvenile-onset; Parkinson disease, type 19B, early-onset |
| DNAL1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 16 |
| DNASE1L3 | Systemic lupus erythematosus 16 |
| DNM1L | Encephalopathy due to defective mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission, type 1 |
| DNM2 | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome, type 5 |
| DNMT3B | Immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies syndrome, type 1 |
| DOCK2 | Immunodeficiency, type 40 |
| DOCK6 | Adams-Oliver syndrome 2 |
| DOCK7 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 23 |
| DOCK8 | Hyper-IgE recurrent infection syndrome, autosomal recessive |
| DOK7 | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, type 3; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 10 |
| DOLK | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1M |
| DONSON | Microcephaly, short stature, and limb abnormalities |
| DPAGT1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1J; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 13 |
| DPH1 | Developmental delay with short stature, dysmorphic features, and sparse hair |
| DPM1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1E |
| DPM2 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type Iu |
| DPM3 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type Io |
| DPY19L2 | Spermatogenic failure, type 9 |
| DPYD | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency |
| DPYS | Dihydropyrimidinuria |
| DRAM2 | Cone-rod dystrophy 21 |
| DRC1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 21 |
| DSG1 | Erythroderma, congenital, with palmoplantar keratoderma, hypotrichosis, and hyper IgE |
| DSG4 | Hypotrichosis, type 6 |
| DSP | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, with woolly hair and keratoderma; Epidermolysis bullosa, lethal acantholytic |
| DST | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| DSTYK | Spastic paraplegia, type 23 autosomal recessive |
| DTNBP1 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 7 |
| DUOX2 | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis, type 6 |
| DUOXA2 | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis, type 5 |
| DYM | Smith-McCort dysplasia; Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen disease |
| DYNC2H1 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia, type 3 with or without polydactyly |
| DYNC2I1 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 8 with or without polydactyly |
| DYNC2I2 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 11 with or without polydactyly |
| DYNC2LI1 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 15 with polydactyly |
| DYNLT2B | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 17 with or without polydactyly |
| DYSF | Miyoshi muscular dystrophy, type 1; Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 2 (LGMD R2) |
| DZIP1L | Polycystic kidney disease 5 |
| EARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 12 |
| ECEL1 | Arthrogryposis, distal, type 5D |
| ECHS1 | Mitochondrial short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase 1 deficiency |
| ECM1 | Urbach-Wiethe disease |
| EDA | Ectodermal dysplasia, type 1 hypohidrotic, X-linked |
| EDAR | Ectodermal dysplasia 10B, hypohidrotic/hair/tooth type |
| EDARADD | Ectodermal dysplasia 11B, hypohidrotic/hair/tooth type |
| EDN1 | Auriculocondylar syndrome, type 3 |
| EDN3 | Waardenburg syndrome, type 4B |
| EDNRB | ABCD syndrome |
| EFEMP2 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 1B |
| EFL1 | Shwachman-Diamond syndrome 2 |
| EGFR | Inflammatory skin and bowel disease, neonatal, 2 |
| EGR2 | Dejerine-Sottas disease |
| EIF2AK3 | Wolcott-Rallison syndrome |
| EIF2AK4 | Pulmonary venoocclusive disease 2 |
| EIF2B1 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B2 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B3 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B4 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B5 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF4A3 | Robin sequence with cleft mandible and limb anomalies |
| ELAC2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 17 |
| ELMO2 | Vascular malformation, primary intraosseous |
| ELOVL4 | Ichthyosis, spastic quadriplegia, and intellectual developmental disorder |
| ELP2 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 58 |
| EMC1 | Cerebellar atrophy, visual impairment, and psychomotor retardation |
| EMD | Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, type 1 X-linked |
| EML1 | Band heterotopia |
| EMP2 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 10 |
| ENAM | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 1C |
| ENO3 | Glycogen storage disease XIII |
| ENPP1 | Arterial calcification, generalized, of infancy, type 1 |
| ENTPD1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 64 autosomal recessive |
| EOGT | Adams-Oliver syndrome 4 |
| EPB41 | Elliptocytosis, type 1 |
| EPB42 | Spherocytosis, type 5 |
| EPCAM | Diarrhea 5 with tufting enteropathy, congenital |
| EPG5 | Vici syndrome |
| EPM2A | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 2A (Lafora) |
| EPRS1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 15 |
| EPS8L2 | Deafness autosomal recessive, type 106 |
| ERAL1 | Perrault syndrome 6 |
| ERBB3 | Lethal congenital contractural syndrome, type 2 |
| ERCC1 | Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome, type 4 |
| ERCC2 | Trichothiodystrophy, type 1 |
| ERCC3 | Trichothiodystrophy, type 2 |
| ERCC4 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group Q |
| ERCC5 | Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome, type 3 |
| ERCC6 | Cockayne syndrome, type B; Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome, type 1 |
| ERCC6L2 | Bone marrow failure syndrome, type 2 |
| ERCC8 | Cockayne syndrome, type A |
| ERLIN1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 62 autosomal recessive |
| ERLIN2 | Spastic paraplegia, type 18 autosomal recessive |
| ESCO2 | Roberts syndrome; Juberg-Hayward syndrome |
| ESPN | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 36 |
| ESR1 | Estrogen resistance |
| ESRRB | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 35 |
| ETFA | Glutaric acidemia, type 2A |
| ETFB | Glutaric acidemia, type 2B |
| ETFDH | Glutaric acidemia, type 2C |
| ETHE1 | Ethylmalonic encephalopathy |
| EVC | Ellis-van Creveld syndrome |
| EVC2 | Ellis-van Creveld syndrome |
| EXOSC3 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 1B |
| EXPH5 | Epidermolysis bullosa, nonspecific, autosomal recessive |
| EXT1 | Chondrosarcoma |
| EXTL3 | Immunoskeletal dysplasia with neurodevelopmental abnormalities |
| EYS | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 25 |
| F10 | Factor X deficiency |
| F11 | Factor XI deficiency |
| F13A1 | Factor XIIIA deficiency |
| F13B | Factor XIIIB deficiency |
| F2 | Prothrombin deficiency |
| F5 | Factor V deficiency |
| F7 | Factor VII deficiency |
| F8 | Hemophilia A |
| F9 | Hemophilia B |
| FA2H | Spastic paraplegia, type 35 autosomal recessive |
| FADD | Infections, recurrent, with encephalopathy, hepatic dysfunction, and cardiovascular malformations |
| FAH | Tyrosinemia, type 1 |
| FAM126A | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 5 |
| FAM161A | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 28 |
| FAM20A | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 1G (Enamel-renal syndrome) |
| FAM20C | Raine syndrome |
| FAN1 | Interstitial nephritis, karyomegalic |
| FANCA | Fanconi anemia, complementation group A |
| FANCB | Fanconi anemia, complementation group B |
| FANCC | Fanconi anemia, complementation group C |
| FANCD2 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group D2 |
| FANCE | Fanconi anemia, complementation group E |
| FANCF | Fanconi anemia, complementation group F |
| FANCG | Fanconi anemia, complementation group G |
| FANCI | Fanconi anemia, complementation group I |
| FANCL | Fanconi anemia, complementation group L |
| FANCM | Spermatogenic failure, type 28 |
| FAR1 | Peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA reductase 1 disorder |
| FARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 14; Spastic paraplegia, type 77 autosomal recessive |
| FASTKD2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 44 |
| FAT4 | Hennekam lymphangiectasia-lymphedema syndrome 2 |
| FBLN5 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 1A |
| FBP1 | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency |
| FBXL4 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 13 (encephalomyopathic type) |
| FBXO7 | Parkinson disease, type 15 autosomal recessive |
| FDXR | Auditory neuropathy and optic atrophy |
| FECH | Protoporphyria, erythropoietic, autosomal recessive |
| FERMT1 | Kindler syndrome |
| FERMT3 | Leukocyte adhesion deficiency, type 3 |
| FEZF1 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism type 22 with or without anosmia |
| FGA | Afibrinogenemia, congenital |
| FGB | Congenital afibrinogenemia |
| FGD1 | Aarskog-Scott syndrome; intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, type 16 |
| FGD4 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4H |
| FGF23 | Tumoral calcinosis, hyperphosphatemic, familial, type 2 |
| FGF3 | Deafness, congenital with inner ear agenesis, microtia, and microdontia |
| FGG | Afibrinogenemia, congenital; Hypofibrinogenemia, congenital |
| FH | Fumarase deficiency |
| FHL1 | Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 6, X-linked |
| FIBP | Thauvin-Robinet-Faivre syndrome |
| FIG4 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4J; Yunis-Varon syndrome |
| FKBP10 | Bruck syndrome 1 |
| FKBP14 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, kyphoscoliotic type, 2 |
| FKRP | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 5A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 5B; Type 5C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 9 [LGMDR9]) |
| FKTN | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 4A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 4B; Type 4C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 13 [LGMD R13]) |
| FLAD1 | Lipid storage myopathy due to flavin adenine dinucleotide synthetase deficiency |
| FLG | Ichthyosis vulgaris |
| FLI1 | Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, type 21 |
| FLNA | X-linked otopalatodigital (X-OPD) spectrum disorders; |
| FLNB | Spondylocarpotarsal synostosis syndrome |
| FLVCR1 | Posterior column ataxia-retinitis pigmentosa syndrome |
| FLVCR2 | Proliferative vasculopathy and hydranencephaly-hydrocephaly syndrome |
| FMN2 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 47 |
| FMO3 | Trimethylaminuria |
| FMR1 | Fragile X syndrome |
| FOLR1 | Neurodegeneration due to cerebral folate transport deficiency |
| FOXE1 | Bamforth-Lazarus syndrome |
| FOXE3 | Anterior segment dysgenesis, type 2 multiple subtypes |
| FOXN1 | T-cell immunodeficiency, congenital alopecia and nail dystrophy |
| FOXP3 | Immunodysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, and enteropathy, X-linked |
| FOXRED1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 19 |
| FRAS1 | Fraser syndrome, type 1 |
| FREM1 | Manitoba oculotrichoanal syndrome |
| FREM2 | Fraser syndrome, type 2 |
| FRRS1L | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 37 |
| FSHB | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 24 without anosmia |
| FSHR | Ovarian dysgenesis 1 |
| FTCD | Glutamate formiminotransferase deficiency |
| FTL | L-ferritin deficiency |
| FTO | Growth retardation, developmental delay, facial dysmorphism |
| FTSJ1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 9 |
| FUCA1 | Fucosidosis |
| FUT8 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation with defective fucosylation, type 1 |
| FXN | Friedreich ataxia |
| FYCO1 | Cataract 18 |
| FZD6 | Nail disorder, nonsyndromic congenital, type 10 (claw-shaped nails) |
| G6PC | Glycogen storage disease, type 1A |
| G6PC3 | Dursun syndrome |
| G6PD | Hemolytic anemia, G6PD deficient (favism) |
| GAA | Glycogen storage disease, type 2 |
| GALC | Krabbe disease |
| GALE | Galactose epimerase deficiency |
| GALK1 | Galactokinase deficiency with cataracts |
| GALNS | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 4A |
| GALNT3 | Tumoral calcinosis, hyperphosphatemic, familial, type 1 |
| GALT | Galactosemia |
| GAMT | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome, type 2 |
| GAN | Giant axonal neuropathy, type 1 |
| GAS8 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 33 |
| GATM | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome, type 3 |
| GBA | Gaucher Disease |
| GBA2 | Spastic paraplegia, type 46 autosomal recessive |
| GBE1 | Glycogen storage disease, type 4 |
| GCDH | Glutaricaciduria, type 1 |
| GCH1 | Hyperphenylalaninemia, BH4-deficient, type B |
| GCK | Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) |
| GCM2 | Hypoparathyroidism, familial isolated (FIH) 2 |
| GCNT2 | Cataract 13 with adult i phenotype |
| GCSH | ?Glycine encephalopathy |
| GDAP1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, recessive intermediate, type A |
| GDF1 | Right atrial isomerism (Ivemark syndrome) |
| GDF5 | Chondrodysplasia, Grebe type |
| GDF6 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 17 |
| GDI1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 41 |
| GFER | Myopathy, mitochondrial progressive, with congenital cataract, hearing loss, and developmental delay |
| GFM1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency, type 1 |
| GFPT1 | Myasthenia, congenital, type 12 with tubular aggregates |
| GGCX | Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, combined deficiency of, type 1 |
| GH1 | Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, type 1A; Kowarski syndrome |
| GHR | Laron dwarfism |
| GHRHR | Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, type 1B |
| GHSR | Growth hormone deficiency, isolated partial |
| GINS1 | Immunodeficiency, type 55 |
| GIPC3 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 15 |
| GJA1 | Craniometaphyseal dysplasia, autosomal recessive |
| GJB1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, X-linked dominant, type 1 |
| GJB2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 1A; Deafness, digenic, GJB2/GJB6 |
| GJB6 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 1B; Deafness, digenic GJB2/GJB6 |
| GJC2 | Spastic paraplegia, type 44 autosomal recessive |
| GK | Glycerol kinase deficiency |
| GLA | Fabry disease |
| GLB1 | GM1-gangliosidosis, types 1-3; Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 4B (Morquio) |
| GLDC | Glycine encephalopathy |
| GLDN | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 11 |
| GLE1 | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome, type 1; Congenital arthrogryposis with anterior horn cell disease |
| GLIS2 | Nephronophthisis, type 7 |
| GLIS3 | Diabetes mellitus, neonatal, with congenital hypothyroidism |
| GLRA1 | Hyperekplexia, type 1 |
| GLRB | Hyperekplexia, type 2 |
| GLRX5 | Anemia, sideroblastic, type 3 pyridoxine-refractory; Spasticity, childhood-onset, with hyperglycinemia |
| GLUL | Glutamine deficiency, congenital |
| GLYCTK | D-glyceric aciduria |
| GM2A | GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant |
| GMPPA | Alacrima, achalasia, and intellectual developmental disorder syndrome |
| GMPPB | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy 14 |
| GNAT1 | Night blindness, congenital stationary, type 1G |
| GNAT2 | Achromatopsia, type 4 |
| GNB5 | Intellectual developmental disorder with cardiac arrhythmia; Language delay and ADHD/cognitive impairment with or without cardiac arrhythmia |
| GNE | Inclusion body myopathy, type 2 (Nonaka myopathy) |
| GNMT | Glycine N-methyltransferase deficiency |
| GNPAT | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 2 |
| GNPTAB | Mucolipidosis 2 alpha/beta; Mucolipidosis 3 alpha/beta |
| GNPTG | Mucolipidosis III gamma |
| GNRHR | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 7 without anosmia |
| GNS | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 3D (Sanfilippo syndrome D) |
| GORAB | Geroderma osteodysplasticum |
| GOSR2 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 6 |
| GOT2 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 82 |
| GP1BA | Bernard-Soulier syndrome, type A1 |
| GP1BB | Bernard-Soulier syndrome, type B |
| GP6 | Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, type 11 |
| GP9 | Bernard-Soulier syndrome, type C |
| GPAA1 | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis defect 15 |
| GPC3 | Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, type 1 |
| GPC6 | Omodysplasia, type 1 |
| GPD1 | Hypertriglyceridemia, transient infantile |
| GPHN | Molybdenum cofactor deficiency C |
| GPI | Hemolytic anemia, nonspherocytic, due to glucose phosphate isomerase deficiency |
| GPIHBP1 | Hyperlipoproteinemia, type 1D |
| GPR143 | Ocular albinism, type 1 (Nettleship-Falls type) |
| GPR179 | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), type 1E, autosomal recessive |
| GPR68 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 2A6 (hypomaturation type) |
| GPR98 | Usher syndrome, type 2C |
| GPSM2 | Chudley-McCullough syndrome |
| GPT2 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 49 |
| GPX4 | Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, Sedaghatian type |
| GRHL2 | Ectodermal dysplasia/short stature syndrome |
| GRHPR | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 2 |
| GRIA3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Wu type |
| GRID2 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 18 |
| GRIK2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 6 |
| GRIN1 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with or without hyperkinetic movements and seizures, autosomal recessive |
| GRIP1 | Fraser syndrome 3 |
| GRK1 | Oguchi disease-2 |
| GRM1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 13 |
| GRM6 | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), type 1B, autosomal recessive |
| GRN | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 11 |
| GRXCR1 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 25 |
| GSC | Short stature, auditory canal atresia, mandibular hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities |
| GSS | Glutathione synthetase deficiency |
| GTF2H5 | Trichothiodystrophy, type 3 photosensitive |
| GTPBP2 | Jaberi-Elahi syndrome |
| GTPBP3 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 23 |
| GUCY2C | Meconium ileus |
| GUCY2D | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 1 |
| GUF1 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 40 |
| GUSB | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 7 |
| GYG1 | Polyglucosan body myopathy, type 2 |
| GYS1 | Glycogen storage disease, type 0 muscle |
| GYS2 | Glycogen storage disease, type 0 liver |
| GZF1 | Joint laxity, short stature, and myopia |
| H6PD | Cortisone reductase deficiency 1 |
| HAAO | Vertebral, cardiac, renal, and limb defects syndrome 1 |
| HACE1 | Spastic paraplegia and psychomotor retardation with or without seizures |
| HADH | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| HADHA | Long-chain 3-hydroxyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency; Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency |
| HADHB | Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency |
| HAMP | Hemochromatosis, type 2B |
| HARS1 | Usher syndrome, type 3B |
| HAX1 | Neutropenia, severe congenital, type 3 autosomal recessive |
| HBA1 | Alpha-thalassemia |
| HBA2 | Alpha-thalassemia |
| HBB | Beta-thalassemia, Sickle cell anemia and other HBB-related hemoglobinopathies |
| HCCS | Linear skin defects with multiple congenital anomalies 1 |
| HCFC1 | intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 3 (methylmalonic acidemia and homocysteinemia, cblX type ) |
| HELLS | Immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies syndrome 4 |
| HEPACAM | Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts 2A |
| HERC1 | Macrocephaly, dysmorphic facies, and psychomotor retardation |
| HERC2 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 38 |
| HES7 | Spondylocostal dysostosis, type 4 autosomal recessive |
| HESX1 | Growth hormone deficiency with pituitary anomalies |
| HEXA | Tay-Sachs disease |
| HEXB | Sandhoff disease, infantile, juvenile, and adult forms |
| HFE | Hemochromatosis |
| HFE2 | Hemochromatosis, type 2A |
| HFM1 | Premature ovarian failure 9 |
| HGD | Alkaptonuria |
| HGF | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 39 |
| HGSNAT | Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3C (Sanfilippo syndrome C) |
| HIBCH | 3-hydroxyisobutryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency |
| HIKESHI | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 13 |
| HINT1 | Neuromyotonia and axonal neuropathy, autosomal recessive |
| HJV | Hemochromatosis, type 2A |
| HK1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4G |
| HLCS | Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency |
| HMGCL | HMG-CoA lyase deficiency |
| HMGCS2 | HMG-CoA synthase-2 deficiency |
| HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase-1 deficiency |
| HMX1 | Oculoauricular syndrome |
| HNMT | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 51 |
| HOGA1 | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 3 |
| HOXA1 | Athabaskan brainstem dysgenesis syndrome |
| HOXB1 | Facial paresis, hereditary congenital, 3 |
| HOXC13 | Ectodermal dysplasia 9 hair/nail type |
| HPCA | Dystonia 2 torsion, autosomal recessive |
| HPD | Tyrosinemia, type 3 |
| HPGD | Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, primary, type 1 (pachydermoperiostosis) |
| HPRT1 | Lesch-Nyhan syndrome |
| HPS1 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 1 |
| HPS3 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 3 |
| HPS4 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 4 |
| HPS5 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 5 |
| HPS6 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 6 |
| HPSE2 | Urofacial syndrome, type 1 |
| HR | Alopecia universalis; Atrichia with papular lesions |
| HSD11B2 | Apparent mineralocorticoid excess |
| HSD17B10 | HSD10 mitochondrial disease |
| HSD17B3 | 46,XY disorder of sex development due to 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3 deficiency |
| HSD17B4 | D-bifunctional protein deficiency |
| HSD3B2 | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency |
| HSD3B7 | Bile acid synthesis defect, congenital, type 1 |
| HSPA9 | Even-plus syndrome |
| HSPD1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 4 |
| HSPG2 | Dyssegmental dysplasia, Silverman-Handmaker type |
| HTRA1 | CARASIL syndrome |
| HTRA2 | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 8 |
| HUWE1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Turner type |
| HYAL1 | ?Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 9 |
| HYDIN | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 5 |
| HYLS1 | Hydrolethalus syndrome |
| IARS1 | Growth retardation, intellectual developmental disorder, hypotonia, and hepatopathy |
| IBA57 | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 3 |
| ICOS | Immunodeficiency, common variable, 1 |
| IDH3B | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 46 |
| IDS | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 2 |
| IDUA | Mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 |
| IER3IP1 | Microcephaly, epilepsy, and diabetes syndrome |
| IFNGR1 | Immunodeficiency, type 27A, mycobacteriosis |
| IFNGR2 | Immunodeficiency, type 28 mycobacteriosis |
| IFT122 | Cranioectodermal dysplasia 1 |
| IFT140 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 80; Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 9 with or without polydactyly |
| IFT172 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 10 with or without polydactyly |
| IFT43 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 18 with polydactyly |
| IFT52 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 16 with or without polydactyly |
| IFT80 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia, type 2 with or without polydactyly |
| IFT81 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 19 with or without polydactyly |
| IGBP1 | Corpus callosum, agenesis of, with impaired intellectual development, ocular coloboma and micrognathia |
| IGF1 | Growth retardation with deafness and intellectual developmental disorder due to IGF1 deficiency |
| IGF1R | Insulin-like growth factor I, resistance to |
| IGFALS | Acid-labile subunit deficiency |
| IGFBP7 | Retinal arterial macroaneurysm with supravalvular pulmonic stenosis |
| IGHMBP2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2S |
| IGLL1 | Agammaglobulinemia 2 |
| IGSF1 | Hypothyroidism, central, and testicular enlargement |
| IHH | Acrocapitofemoral dysplasia |
| IKBKAP | Dysautonomia, familial |
| IKBKB | Immunodeficiency, type 15 |
| IKBKG | Ectodermal dysplasia and immunodeficiency 1 |
| IL10RA | Inflammatory bowel disease, type 28 early onset, autosomal recessive |
| IL10RB | Inflammatory bowel disease, type 25 early onset, autosomal recessive |
| IL11RA | Craniosynostosis and dental anomalies |
| IL12B | Immunodeficiency, type 29 mycobacteriosis |
| IL12RB1 | Immunodeficiency, type 30 |
| IL17RA | Immunodeficiency, type 51 |
| IL17RC | Candidiasis, familial, 9 |
| IL1RAPL1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 21 |
| IL1RN | Sterile multifocal osteomyelitis with periostitis and pustulosis |
| IL21R | Immunodeficiency, type 56 |
| IL2RA | Immunodeficiency, type 41 with lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity |
| IL2RG | Severe combined immunodeficiency, X-linked |
| IL36RN | Psoriasis, type 14 pustular |
| IL7R | Severe combined immunodeficiency, T-cell negative, B-cell/natural killer cell-positive type |
| ILDR1 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 42 |
| IMPA1 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 59 |
| IMPG2 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 56 |
| INPP5E | Joubert syndrome, type 1 |
| INPP5K | Muscular dystrophy, congenital, with cataracts and intellectual disability |
| INPPL1 | Opsismodysplasia |
| INS | Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) |
| INSR | Diabetes mellitus, insulin-resistant, with acanthosis nigricans, type A |
| INTS1 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with cataracts, poor growth, and dysmorphic facies |
| INVS | Nephronophthisis, type 2 infantile |
| IQCB1 | Senior-Loken syndrome, type 5 |
| IQCE | Polydactyly, postaxial, type A7 |
| IQSEC2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 1 |
| IRAK4 | Immunodeficiency, type 67 (IRAK4 deficiency) |
| IRF8 | Immunodeficiency, type 32B, monocyte and dendritic cell deficiency |
| IRX5 | Hamamy syndrome |
| ISCA1 | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 5 |
| ISCA2 | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 4 |
| ISCU | Myopathy with lactic acidosis, hereditary |
| ISG15 | Immunodeficiency, type 38 |
| ITCH | Autoimmune disease, multisystem, with facial dysmorphism |
| ITGA2B | Glanzmann thrombasthenia |
| ITGA3 | Interstitial lung disease, nephrotic syndrome, and epidermolysis bullosa, congenital |
| ITGA6 | Epidermolysis bullosa, junctional, with pyloric stenosis |
| ITGA7 | Muscular dystrophy, congenital, due to ITGA7 deficiency |
| ITGA8 | Renal hypodysplasia/aplasia 1 |
| ITGB2 | Leukocyte adhesion deficiency |
| ITGB3 | Glanzmann thrombasthenia |
| ITGB4 | Epidermolysis bullosa, junctional, with pyloric atresia |
| ITGB6 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 1H |
| ITK | Lymphoproliferative syndrome 1 |
| ITPA | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 35 |
| ITPR1 | Gillespie syndrome |
| IVD | Isovaleric acidemia |
| IYD | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis, type 4 |
| JAGN1 | Neutropenia, severe congenital, 6 autosomal recessive |
| JAK3 | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, autosomal recessive, T-negative/B-positive type |
| JAM3 | Hemorrhagic destruction of the brain, subependymal calcification, and cataracts |
| JUP | Naxos disease |
| KANK2 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 16 |
| KARS1 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 89 |
| KATNB1 | Lissencephaly 6 with microcephaly |
| KATNIP | Joubert syndrome 26 |
| KCNE1 | Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome 2 |
| KCNJ1 | Bartter syndrome, type 2 |
| KCNJ10 | SESAME syndrome |
| KCNJ11 | Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, type 2 (congenital hyperinsulinism); Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) |
| KCNJ13 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 16 |
| KCNV2 | Retinal cone dystrophy, type 3B |
| KCTD7 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 3 with or without intracellular inclusions |
| KDM5C | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Claes-Jensen type |
| KDSR | Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 4 |
| KERA | Cornea plana 2 autosomal recessive |
| KHDC3L | Hydatidiform mole, recurrent, type 2 |
| KIAA0586 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 14 with polydactyly |
| KIAA0753 | Orofaciodigital syndrome, type 15 |
| KIAA1109 | Alkuraya-Kucinskas syndrome |
| KIAA1549 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 86 |
| KIAA2022 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 98 |
| KIF14 | Microcephaly 20 primary, autosomal recessive; ?Meckel syndrome 12 |
| KIF1A | Neuropathy, hereditary sensory, type 2C; Spastic paraplegia, type 30 autosomal recessive |
| KIF1C | Spastic ataxia 2 autosomal recessive |
| KIF7 | Acrocallosal syndrome; Joubert syndrome, type 12 |
| KIFBP | Goldberg-Shprintzen megacolon syndrome |
| KISS1R | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 8 with or without anosmia |
| KIZ | Retinitis pigmentosa 69 |
| KLHL3 | Pseudohypoaldosteronism, type 2D |
| KLHL40 | Nemaline myopathy 8 autosomal recessive |
| KLHL41 | Nemaline myopathy 9 |
| KLHL7 | Cold-induced sweating syndrome 3 |
| KLK4 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 2A1 (hypomaturation type) |
| KLKB1 | Fletcher factor (prekallikrein) deficiency |
| KNL1 | Microcephaly 4 primary, autosomal recessive |
| KPTN | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 41 |
| KREMEN1 | Ectodermal dysplasia 13 hair/tooth type |
| KRT10 | Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis |
| KRT14 | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| KRT25 | Woolly hair, autosomal recessive 3 |
| KRT5 | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| KRT85 | Ectodermal dysplasia 4 hair/nail type |
| KY | Myopathy, myofibrillar, type 7 |
| KYNU | Vertebral, cardiac, renal, and limb defects syndrome, type 2 |
| L1CAM | L1 Syndrome |
| L2HGDH | L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria |
| LAMA1 | Poretti-Boltshauser syndrome |
| LAMA2 | LAMA2-related muscular dystrophy |
| LAMA3 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type; JEB non-Herlitz type |
| LAMB1 | Lissencephaly, type 5 |
| LAMB2 | Pierson syndrome; Nephrotic syndrome, type 5 with or without ocular abnormalities |
| LAMB3 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type; JEB non-Herlitz type |
| LAMC2 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type; JEB non-Herlitz type |
| LAMC3 | Cortical malformations, occipital |
| LAMP2 | Danon disease |
| LARGE1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 6A and 6B |
| LARP7 | Alazami syndrome |
| LARS1 | Infantile liver failure syndrome 1 (ILFS1) |
| LARS2 | Perrault syndrome, type 4 |
| LAT | Immunodeficiency, type 52 |
| LBR | Greenberg skeletal dysplasia |
| LCA5 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 5 |
| LCAT | Familial LCAT deficiency; Fish-eye disease |
| LCK | Immunodeficiency, type 22 |
| LCT | Lactase deficiency, congenital |
| LDHA | Glycogen storage disease type 11 |
| LDLRAP1 | Hypercholesterolemia, familial, autosomal recessive |
| LEMD2 | Cataract 46 juvenile-onset |
| LEP | Obesity, morbid, due to leptin deficiency |
| LEPR | Obesity, morbid, due to leptin receptor deficiency |
| LGI4 | Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, neurogenic, with myelin defect |
| LHB | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 23 with or without anosmia |
| LHCGR | Leydig cell hypoplasia |
| LHFPL5 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 67 |
| LHX3 | Pituitary hormone deficiency, combined, type 3 |
| LIAS | Hyperglycinemia, lactic acidosis, and seizures |
| LIFR | Stuve-Wiedemann syndrome / Schwartz-Jampel type 2 syndrome |
| LIG4 | LIG4 syndrome |
| LIM2 | Cataract 19 multiple types |
| LINS1 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 27 |
| LIPA | Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency |
| LIPE | Lipodystrophy, familial partial, type 6 |
| LIPH | Hypotrichosis, type 7 or woolly hair, autosomal recessive, type 2 with or without hypotrichosis |
| LIPN | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 8 |
| LIPT1 | Lipoyltransferase 1 deficiency |
| LIPT2 | Encephalopathy, neonatal severe, with lactic acidosis and brain abnormalities |
| LMAN1 | Combined deficiency of factor V and factor VIII, type 1 |
| LMBRD1 | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblF type |
| LMF1 | Lipase deficiency, combined |
| LMNA | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1A |
| LMOD3 | Nemaline myopathy 10 |
| LONP1 | CODAS syndrome |
| LOXHD1 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 77 |
| LPAR6 | Hypotrichosis, type 8 or woolly hair, autosomal recessive, type 1 with or without hypotrichosis |
| LPIN1 | Myoglobinuria, acute recurrent, autosomal recessive |
| LPIN2 | Majeed syndrome |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase deficiency |
| LRAT | Leber congenital amaurosis type 14 |
| LRBA | Immunodeficiency, common variable, 8 with autoimmunity |
| LRIG2 | Urofacial syndrome 2 |
| LRIT3 | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), 1F, autosomal recessive |
| LRMDA | Albinism, oculocutaneous, type 7 |
| LRP2 | Donnai-Barrow syndrome |
| LRP4 | Cenani-Lenz syndactyly syndrome |
| LRP5 | Osteoporosis-pseudoglioma syndrome |
| LRPAP1 | Myopia, type 23 autosomal recessive |
| LRPPRC | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 5, (French-Canadian) |
| LRRC6 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 19 |
| LRSAM1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2P |
| LRTOMT | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 63 |
| LSS | Cataract 44 |
| LTBP2 | Microspherophakia and/or megalocornea, with ectopia lentis and with or without secondary glaucoma |
| LTBP3 | Dental anomalies and short stature |
| LTBP4 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 1C |
| LYRM7 | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 8 |
| LYST | Chediak-Higashi syndrome |
| LZTFL1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 17 |
| LZTR1 | Noonan syndrome, type 2 |
| MAG | Spastic paraplegia, type 75 autosomal recessive |
| MAGI2 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 15 |
| MAGT1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type Icc |
| MAK | Retinitis pigmentosa type 62 |
| MALT1 | Immunodeficiency, type 12 |
| MAN1B1 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 15 |
| MAN2B1 | Alpha-mannosidosis |
| MANBA | Mannosidosis, beta |
| MAP3K20 | Centronuclear myopathy, type 6 with fiber-type disproportion |
| MAPKBP1 | Nephronophthisis 20 |
| MAPT | Supranuclear palsy, progressive atypical (parkinsonism syndrome) |
| MARS1 | Interstitial lung and liver disease |
| MARS2 | Spastic ataxia, type 3 autosomal recessive |
| MARVELD2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 49 |
| MASP1 | 3MC syndrome 1 |
| MAT1A | Methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency, autosomal recessive |
| MATN3 | Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Borochowitz-Cormier-Daire type |
| MBOAT7 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 57 |
| MBTPS2 | Olmsted syndrome, X-linked |
| MC2R | Glucocorticoid deficiency, due to ACTH unresponsiveness |
| MCCC1 | 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency, type 1 |
| MCCC2 | 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency, type 2 |
| MCEE | Methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase deficiency |
| MCFD2 | Combined deficiency of factor V and factor VIII, type 2 |
| MCIDAS | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 42 |
| MCM3AP | Peripheral neuropathy, autosomal recessive, with or without impaired intellectual development |
| MCM4 | Immunodeficiency, type 54 |
| MCM9 | Ovarian dysgenesis 4 |
| MCOLN1 | Mucolipidosis type 4 |
| MCPH1 | Microcephaly type 1 primary, autosomal recessive |
| MDH2 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 51 |
| MECP2 | Encephalopathy, neonatal severe; Rett syndrome |
| MECR | Dystonia, childhood-onset, with optic atrophy and basal ganglia abnormalities |
| MED17 | Microcephaly, postnatal progressive, with seizures and brain atrophy |
| MED23 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 18 |
| MED25 | Basel-Vanagait-Smirin-Yosef syndrome |
| MEFV | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| MEGF10 | Myopathy, areflexia, respiratory distress, and dysphagia, early-onset |
| MEGF8 | Carpenter syndrome, type 2 |
| MEOX1 | Klippel-Feil syndrome 2 |
| MERTK | Retinitis pigmentosa type 38 |
| MESP2 | Spondylocostal dysostosis, type 2 autosomal recessive |
| METTL23 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 44 |
| MFF | Encephalopathy due to defective mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission, type 2 |
| MFN2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2A2B |
| MFRP | Microphthalmia, isolated type 5 |
| MFSD2A | Microcephaly 15 primary, autosomal recessive |
| MFSD8 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 7 |
| MGAT2 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2a |
| MGME1 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 11 |
| MGP | Keutel syndrome |
| MICU1 | Myopathy with extrapyramidal signs |
| MID1 | Opitz GBBB syndrome, type 1 |
| MIPEP | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 31 |
| MITF | COMMAD syndrome |
| MKKS | Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 6 |
| MKS1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 13; Meckel syndrome, type 1; Joubert syndrome, type 28 |
| MLC1 | Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts |
| MLPH | Griscelli syndrome, type 3 |
| MLYCD | Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency |
| MMAA | Methylmalonic aciduria, vitamin B12-responsive |
| MMAB | Methylmalonic aciduria, vitamin B12-responsive, type cblB |
| MMACHC | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblC type |
| MMADHC | Homocystinuria, cblD type, variant 1 |
| MME | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2T |
| MMP13 | Metaphyseal dysplasia, Spahr type |
| MMP2 | Multicentric osteolysis, nodulosis, and arthropathy (MONA) |
| MMP20 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 2A2 (hypomaturation type) |
| MMP21 | Heterotaxy, visceral, 7 autosomal |
| MMUT | Methylmalonic aciduria, mut(0) type |
| MOCOS | Xanthinuria, type 2 |
| MOCS1 | Molybdenum cofactor deficiency A |
| MOCS2 | Molybdenum cofactor deficiency B |
| MOGS | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2B |
| MPC1 | Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier deficiency |
| MPDU1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1F |
| MPDZ | Hydrocephalus, congenital, type 2 with or without brain or eye anomalies |
| MPI | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1B |
| MPIG6B | Thrombocytopenia, anemia, and myelofibrosis |
| MPL | Thrombocytopenia, congenital amegakaryocytic |
| MPLKIP | Trichothiodystrophy, type 4 nonphotosensitive |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase deficiency |
| MPV17 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome type 6 (hepatocerebral); Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2EE |
| MPZ | Dejerine-Sottas disease |
| MRAP | Glucocorticoid deficiency, type 2 |
| MRE11 | Ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder 1 |
| MRPS16 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 2 |
| MRPS22 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency type 5 |
| MRPS34 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 32 |
| MSH3 | Familial adenomatous polyposis, type 4 |
| MSMO1 | Microcephaly, congenital cataract, and psoriasiform dermatitis |
| MSRB3 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 74 |
| MSTO1 | Myopathy, mitochondrial, and ataxia |
| MTFMT | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 15 |
| MTHFD1 | Combined immunodeficiency and megaloblastic anemia with or without hyperhomocysteinemia |
| MTHFR | Homocystinuria due to MTHFR deficiency |
| MTM1 | Myotubular myopathy, X-linked |
| MTMR2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4B1 |
| MTO1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 10 |
| MTR | Homocystinuria-megaloblastic anemia, cblG complementation type |
| MTRR | Homocystinuria-megaloblastic anemia, cbl E type |
| MTTP | Abetalipoproteinemia |
| MUSK | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, type 1; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 9 associated with acetylcholine receptor deficiency |
| MUTYH | Adenomas, multiple colorectal |
| MVK | Mevalonic aciduria |
| MYBPC1 | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome, type 4 |
| MYD88 | Immunodeficiency, type 68 |
| MYH2 | Proximal myopathy and ophthalmoplegia |
| MYMK | Carey-Fineman-Ziter syndrome |
| MYO15A | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 3 |
| MYO18B | Klippel-Feil syndrome, type 4 autosomal recessive, with myopathy and facial dysmorphism |
| MYO1E | Glomerulosclerosis, focal segmental, 6 |
| MYO3A | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 30 |
| MYO5A | Griscelli syndrome, type 1 |
| MYO5B | Microvillus inclusion disease |
| MYO6 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 37 |
| MYO7A | Usher syndrome, type 1B; Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| MYPN | Nemaline myopathy, type 11 autosomal recessive |
| NADK2 | 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase deficiency |
| NAGA | Schindler disease, type I |
| NAGLU | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 3B (Sanfilippo B) |
| NAGS | N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency |
| NALCN | Hypotonia, infantile, with psychomotor retardation and characteristic facies 1 |
| NANS | Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Camera-Genevieve type |
| NARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 24 |
| NAXE | Encephalopathy, progressive, early-onset, with brain edema and/or leukoencephalopathy |
| NBAS | Infantile liver failure syndrome, type 2; Short stature, optic nerve atrophy, and Pelger-Huet anomaly |
| NBEAL2 | Gray platelet syndrome |
| NBN | Nijmegen breakage syndrome |
| NCAPD3 | Microcephaly 22 primary, autosomal recessive |
| NCF1 | Chronic granulomatous disease, type 1 |
| NCF2 | Chronic granulomatous disease, type 2 |
| NCF4 | Chronic granulomatous disease 3 autosomal recessive |
| NDE1 | Lissencephaly, type 4 (with microcephaly) |
| NDP | Norrie disease |
| NDRG1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4D |
| NDST1 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 46 |
| NDUFA1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 12 |
| NDUFA10 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 22 |
| NDUFA11 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 14 |
| NDUFA12 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 23 |
| NDUFA2 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 13 |
| NDUFA9 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 26 |
| NDUFAF1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 11 |
| NDUFAF2 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 10 |
| NDUFAF3 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 18 |
| NDUFAF5 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 16 |
| NDUFAF6 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 17 |
| NDUFB3 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 25 |
| NDUFB9 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 24 |
| NDUFS1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 5 |
| NDUFS2 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 6 |
| NDUFS3 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 8 |
| NDUFS4 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 1 |
| NDUFS6 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 9 |
| NDUFS7 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 3 |
| NDUFS8 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| NDUFV1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 4 |
| NDUFV2 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 7 |
| NEB | Nemaline myopathy type 2 |
| NECTIN1 | Cleft lip/palate-ectodermal dysplasia syndrome; Orofacial cleft 7 |
| NECTIN4 | Ectodermal dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome, type 1 |
| NEFL | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 1F |
| NEK1 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia, type 6 with or without polydactyly |
| NEK8 | Renal-hepatic-pancreatic dysplasia, type 2 |
| NEK9 | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 10 |
| NEU1 | Sialidosis, type 1 and type 2 |
| NEUROG3 | Diarrhea 4 malabsorptive, congenital |
| NFU1 | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 1 |
| NGF | Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, type 5 |
| NGLY1 | Congenital disorder of deglycosylation |
| NHEJ1 | Severe combined immunodeficiency with microcephaly, growth retardation, and sensitivity to ionizing radiation |
| NHLRC1 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 2B (Lafora) |
| NHP2 | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive type 2 |
| NHS | Nance-Horan syndrome; Cataract 40, X-Linked |
| NIN | Seckel syndrome, type 7 |
| NIPAL4 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 6 |
| NKX2-6 | Conotruncal heart malformations |
| NKX3-2 | Spondylo-megaepiphyseal-metaphyseal dysplasia |
| NKX6-2 | Spastic ataxia 8 autosomal recessive, with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy |
| NLRP1 | Autoinflammation with arthritis and dyskeratosis |
| NLRP7 | Hydatidiform mole, recurrent, type 1 |
| NME8 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 6 |
| NMNAT1 | Leber congenital amaurosis type 9 |
| NNT | Glucocorticoid deficiency 4 with or without mineralocorticoid deficiency |
| NONO | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic 34 |
| NOP10 | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive type 1 |
| NPC1 | Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 |
| NPC2 | Niemann-pick disease, type C2 |
| NPHP1 | Joubert syndrome type 4 |
| NPHP3 | Meckel syndrome type 7 |
| NPHP4 | Nephronophthisis type 4 |
| NPHS1 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 1 |
| NPHS2 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 2 |
| NPR2 | Acromesomelic dysplasia, Maroteaux type |
| NR0B1 | Adrenal hypoplasia, congenital |
| NR1H4 | Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, type 5 |
| NR2E3 | Enhanced S-cone syndrome (Goldmann-Favre); Retinitis pigmentosa, type 37 |
| NRL | Retinal degeneration, autosomal recessive, clumped pigment type |
| NRXN1 | Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome, type 2 |
| NSDHL | CHILD syndrome; CK syndrome |
| NSMCE2 | Seckel syndrome, type 10 |
| NSUN2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 5 |
| NT5C2 | Spastic paraplegia, type 45 autosomal recessive |
| NT5C3A | Anemia, hemolytic, due to UMPH1 deficiency |
| NT5E | Calcification of joints and arteries |
| NTHL1 | Familial adenomatous polyposis, type 3 |
| NTRK1 | Insensitivity to pain, congenital, with anhidrosis |
| NUBPL | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 21 |
| NUP107 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 11 |
| NUP62 | Striatonigral degeneration, infantile |
| NUP93 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 12 |
| NYX | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), 1A, X-linked |
| OAT | Gyrate atrophy of choroid and retina |
| OBSL1 | 3M syndrome 2 |
| OCA2 | Oculocutaneous albinism type 2 |
| OCLN | Pseudo-TORCH syndrome, type 1 |
| OCRL | Lowe Syndrome; Dent disease type 2 |
| ODAD1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 20 |
| ODAD2 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 23 |
| ODAD3 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 30 |
| OFD1 | Joubert syndrome 10; Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, type 2 |
| OPA1 | Behr syndrome |
| OPA3 | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 3 |
| OPHN1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Billuart type |
| ORAI1 | Immunodeficiency, type 9 |
| ORC1 | Meier-Gorlin syndrome, type 1 |
| ORC4 | Meier-Gorlin syndrome, type 2 |
| ORC6 | Meier-Gorlin syndrome, type 3 |
| OSGEP | Galloway-Mowat syndrome 3 |
| OSTM1 | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive type 5 |
| OTC | Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency |
| OTOA | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 22 |
| OTOF | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 9 |
| OTOG | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 18B |
| OTOGL | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 84B |
| OTUD6B | Intellectual developmental disorder with dysmorphic facies, seizures, and distal limb anomalies |
| OTULIN | Autoinflammation, panniculitis, and dermatosis syndrome |
| OXCT1 | Succinyl CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase deficiency |
| P2RY12 | Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, type 8 |
| P3H1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 8 |
| P3H2 | Myopia, high, with cataract and vitreoretinal degeneration |
| PADI6 | Preimplantation embryonic lethality 2 |
| PAH | Phenylketonuria |
| PAK3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 30 |
| PALB2 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group N |
| PAM16 | Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, Megarbane-Dagher-Melike type |
| PANK2 | Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation type 1 |
| PAPSS2 | Brachyolmia, type 4 with mild epiphyseal and metaphyseal changes |
| PARK7 | Parkinson disease, type 7 autosomal recessive, early-onset |
| PARN | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive 6 |
| PATL2 | Oocyte maturation defect 4 |
| PAX7 | Rhabdomyosarcoma 2 alveolar |
| PC | Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency |
| PCARE | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 54 |
| PCBD1 | Hyperphenylalaninemia, BH4-deficient, type D |
| PCCA | Propionic acidemia |
| PCCB | Propionic acidemia |
| PCDH12 | Microcephaly, seizures, spasticity, and brain calcification |
| PCDH15 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 23; Usher syndrome, type 1D/F digenic |
| PCDH19 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 9 |
| PCK2 | PEPCK deficiency, mitochondrial |
| PCNT | Microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism, type 2 |
| PCSK1 | Obesity with impaired prohormone processing |
| PCYT1A | Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia with cone-rod dystrophy |
| PDE10A | Dyskinesia, limb and orofacial, infantile-onset |
| PDE6A | Retinitis pigmentosa type 43 |
| PDE6B | Retinitis pigmentosa type 40 |
| PDE6C | Cone dystrophy type 4 |
| PDE6G | Retinitis pigmentosa type 57 |
| PDE6H | Retinal cone dystrophy 3 and achromatopsia 6 |
| PDHA1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-alpha deficiency |
| PDHB | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-beta deficiency |
| PDHX | Lacticacidemia due to PDX1 deficiency |
| PDP1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase deficiency |
| PDSS1 | Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, type 2 |
| PDSS2 | Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, type 3 |
| PDX1 | Pancreatic agenesis type 1 |
| PDXK | Neuropathy, hereditary motor and sensory, type VIC, with optic atrophy |
| PEPD | Prolidase deficiency |
| PET100 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 12 |
| PEX1 | Heimler syndrome type 1 |
| PEX10 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 6A (Zellweger syndrome); Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 6B |
| PEX11B | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder 14B |
| PEX12 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder type 3A (Zellweger) |
| PEX13 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 11A (Zellweger syndrome); Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 11B |
| PEX14 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 13A (Zellweger syndrome) |
| PEX16 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 8A (Zellweger syndrome); Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 8B |
| PEX19 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 12A (Zellweger syndrome) |
| PEX2 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder type 5A (Zellweger) |
| PEX26 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder type 7A (Zellweger) |
| PEX3 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 10A (Zellweger syndrome) |
| PEX5 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder type 2A (Zellweger) |
| PEX6 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 4A (Zellweger syndrome); Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 4B; Heimler syndrome 2 |
| PEX7 | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 1 |
| PFKM | Glycogen storage disease, type 7 |
| PGAM2 | Glycogen storage disease X |
| PGAP1 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 42 |
| PGAP2 | Hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome 3 |
| PGAP3 | Hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome 4 |
| PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 deficiency |
| PGM1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1t |
| PGM3 | Immunodeficiency, type 23 |
| PHF8 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Siderius type |
| PHGDH | Neu-Laxova syndrome, type 1; Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency |
| PHKA1 | Muscle glycogenosis |
| PHKA2 | Glycogen storage disease, type IXa1/2 |
| PHKB | Glycogen storage disease, type 9B |
| PHKG2 | Glycogen storage disease type 9c |
| PHOX2A | Fibrosis of extraocular muscles, congenital, 2 |
| PHYH | Refsum disease |
| PI4KA | Polymicrogyria, perisylvian, with cerebellar hypoplasia and arthrogryposis |
| PIBF1 | Joubert syndrome 33 |
| PIEZO1 | Lymphedema, hereditary, type 3 |
| PIEZO2 | Arthrogryposis, distal, with impaired proprioception and touch |
| PIGC | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis defect 16 |
| PIGG | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 53 |
| PIGL | Zunich neuroectodermal syndrome |
| PIGM | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol deficiency |
| PIGN | Multiple congenital anomalies-hypotonia-seizures syndrome, type 1 |
| PIGO | Hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome 2 |
| PIGT | Multiple congenital anomalies-hypotonia-seizures syndrome 3 |
| PIGV | Hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome 1 |
| PIGW | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis defect 11 |
| PIGY | Hyperphosphatasia with impaired intellectual development syndrome 6 |
| PINK1 | Parkinson disease, type 6 early onset |
| PIP5K1C | Lethal congenital contractural syndrome, type 3 |
| PJVK | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 59 |
| PKD1L1 | Heterotaxy, visceral, 8 autosomal |
| PKHD1 | Polycystic kidney disease type 4 |
| PKLR | Pyruvate kinase deficiency |
| PKP1 | Ectodermal dysplasia/skin fragility syndrome |
| PLA2G6 | Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy type 1 |
| PLAA | Neurodevelopmental disorder with progressive microcephaly, spasticity, and brain anomalies |
| PLCB1 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 12 |
| PLCB4 | Auriculocondylar syndrome, type 2 |
| PLCD1 | Nail disorder, nonsyndromic congenital, type 3 (leukonychia) |
| PLCE1 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 3 |
| PLD1 | Cardiac valvular defect, developmental |
| PLEC | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy |
| PLEKHG5 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, recessive intermediate, type C |
| PLG | Plasminogen deficiency, type I |
| PLK4 | Microcephaly and chorioretinopathy, autosomal recessive, 2 |
| PLOD1 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, kyphoscoliotic type, 1 |
| PLOD2 | Bruck syndrome 2 |
| PLOD3 | Lysyl hydroxylase 3 deficiency |
| PLP1 | Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease |
| PLPBP | Epilepsy, early-onset, vitamin B6-dependent |
| PMM2 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1A |
| PMP22 | Dejerine-Sottas disease |
| PMPCA | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| PMPCB | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 6 |
| PNKP | Ataxia-oculomotor apraxia, type 4; Microcephaly, seizures, and developmental delay |
| PNP | Immunodeficiency due to purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency |
| PNPLA1 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 10 |
| PNPLA2 | Neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy |
| PNPLA6 | Boucher-Neuhauser syndrome; Oliver-McFarlane syndrome; Spastic paraplegia, type 39 autosomal recessive |
| PNPO | Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate oxidase deficiency |
| PNPT1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 13 |
| POC1A | Short stature, onychodysplasia, facial dysmorphism, and hypotrichosis |
| POC1B | Cone-rod dystrophy 20 |
| POLE | FILS syndrome |
| POLG | POLG-related disorders |
| POLH | Xeroderma pigmentosum, variant type |
| POLR1C | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 11; Treacher Collins syndrome 3 |
| POLR1D | Treacher Collins syndrome, type 2 |
| POLR3A | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 7 |
| POLR3B | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 8 |
| POMC | Obesity, adrenal insufficiency, and red hair due to POMC deficiency |
| POMGNT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 3A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 3B; Type 3C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 15 [LGMDR15]) |
| POMGNT2 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 8A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 8C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 24 [LGMD R24]) |
| POMK | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A, 12 |
| POMP | Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma |
| POMT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 1A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 1B; Type 1C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 11 [LGMD R11]) muscular dystrophy, type 11 [LGMD R11]) |
| POMT2 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 2A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 2B; Type 2C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 14 [LGMD R14]) muscular dystrophy, type 14 [LGMD R14]) |
| POP1 | Anauxetic dysplasia, type 2 |
| POR | Antley-Bixler syndrome with genital anomalies and disordered steroidogenesis |
| POU1F1 | Pituitary hormone deficiency, combined, type 1 |
| POU3F4 | Deafness, X-linked, type 2 |
| PPA2 | Sudden cardiac failure, infantile |
| PPIB | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 9 |
| PPM1K | Maple syrup urine disease, mild variant |
| PPP1R15B | Microcephaly, short stature, and impaired glucose metabolism 2 |
| PPT1 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 1 |
| PQBP1 | Renpenning syndrome |
| PRCD | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 36 |
| PRDM12 | Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, type VIII |
| PRDM5 | Brittle cornea syndrome, type 2 |
| PRDX1 | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblC type, digenic |
| PREPL | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 22 |
| PRF1 | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, familial, type 2 |
| PRG4 | Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome |
| PRICKLE1 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 1B |
| PRKCD | Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, type 3 |
| PRKDC | Immunodeficiency 26, with or without neurologic abnormalities |
| PRKN | Parkinson disease, type 2 juvenile |
| PRKRA | Dystonia, type 16 |
| PRMT7 | Short stature, brachydactyly, intellectual developmental disability, and seizures |
| PROC | Thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency, autosomal recessive |
| PRODH | Hyperprolinemia, type 1 |
| PROM1 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 41 |
| PROP1 | Pituitary hormone deficiency, combined, type 2 |
| PROS1 | Thrombophilia due to protein S deficiency, autosomal recessive |
| PRPH2 | Leber congenital amaurosis 18; Retinitis punctata albescens |
| PRPS1 | Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase (PRS) deficiency |
| PRRX1 | Agnathia-otocephaly complex |
| PRSS1 | Trypsinogen deficiency |
| PRSS12 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 1 |
| PRSS56 | Microphthalmia, isolated, type 6 |
| PRUNE1 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with microcephaly, hypotonia, and variable brain anomalies |
| PRX | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4F |
| PSAP | Combined SAP deficiency |
| PSAT1 | Neu-Laxova syndrome, type 2 |
| PSMB8 | Autoinflammation, lipodystrophy, and dermatosis syndrome |
| PSMC3IP | Ovarian dysgenesis 3 |
| PSPH | Phosphoserine phosphatase deficiency |
| PTF1A | Pancreatic agenesis 2 |
| PTH | Hypoparathyroidism, familial isolated, type 1 |
| PTH1R | Chondrodysplasia, Blomstrand type; Eiken syndrome |
| PTPN23 | Neurodevelopmental disorder and structural brain anomalies with or without seizures and spasticity |
| PTPRC | Severe combined immunodeficiency, T cell-negative, B-cell/natural killer-cell positive |
| PTPRO | Nephrotic syndrome, type 6 |
| PTPRQ | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 84A |
| PTRH2 | Infantile-onset multisystem neurologic, endocrine, and pancreatic disease |
| PTS | Hyperphenylalaninemia, BH4-deficient, type A |
| PUS1 | Myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia, type 1 |
| PXDN | Anterior segment dysgenesis, type 7 with sclerocornea |
| PYCR1 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 2B |
| PYCR2 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 10 |
| PYGL | Glycogen storage disease, type 6 |
| PYGM | McArdle disease |
| PYROXD1 | Myopathy, myofibrillar, type 8 |
| QARS1 | Microcephaly, progressive, seizures, and cerebral and cerebellar atrophy |
| QDPR | Hyperphenylalaninemia, BH4-deficient, type C |
| RAB18 | Warburg micro syndrome, type 3 |
| RAB23 | Carpenter syndrome |
| RAB27A | Griscelli syndrome, type 2 |
| RAB28 | Cone-rod dystrophy 18 |
| RAB33B | Smith-McCort dysplasia 2 |
| RAB39B | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 72 |
| RAB3GAP1 | Warburg micro syndrome; Martsolf syndrome |
| RAB3GAP2 | Warburg micro syndrome; Martsolf syndrome |
| RAD50 | Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like disorder |
| RAD51C | Fanconi anemia, complementation group O |
| RAG1 | Omenn syndrome; Severe combined immunodeficiency, B cell-negative |
| RAG2 | Omenn syndrome; Severe combined immunodeficiency, B cell-negative |
| RAPSN | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, type 2; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 11 associated with AChR deficiency |
| RARB | Microphthalmia, syndromic 12 |
| RARS1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 9 |
| RARS2 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 6 |
| RASGRP1 | Immunodeficiency, type 64 |
| RAX | Microphthalmia, syndromic 16 |
| RBBP8 | Jawad syndrome; Seckel syndrome, type 2 |
| RBCK1 | Polyglucosan body myopathy 1 with or without immunodeficiency |
| RBM8A | Thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome |
| RBP3 | Retinitis pigmentosa 66 |
| RBP4 | Retinal dystrophy, iris coloboma, and comedogenic acne syndrome |
| RCBTB1 | Retinal dystrophy with or without extraocular anomalies |
| RD3 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 12 |
| RDH12 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 13 |
| RDH5 | Fundus albipunctatus |
| RDX | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 24 |
| RECQL4 | Baller-Gerold syndrome; RAPADILINO syndrome; Rothmund-Thomson syndrome |
| REEP6 | Retinitis pigmentosa 77 |
| RELN | Lissencephaly 2 (Norman-Roberts type) |
| REN | Renal tubular dysgenesis |
| RETREG1 | Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, type 2B |
| RFT1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type In |
| RFX5 | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 2 |
| RFX6 | Mitchell-Riley syndrome |
| RFXANK | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 2 complementation group B |
| RFXAP | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 2 |
| RHAG | Anemia, hemolytic, Rh-null, regulator type |
| RHO | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 4; Retinitis punctata albescens |
| RIN2 | Macs syndrome |
| RIPK4 | Popliteal pterygium syndrome, Bartsocas-Papas type |
| RIPOR2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 104 |
| RLBP1 | Bothnia retinal dystrophy; Fundus albipunctatus |
| RMND1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 11 |
| RMRP | Anauxetic dysplasia 1 |
| RNASEH1 | Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, autosomal recessive 2 |
| RNASEH2A | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 4 |
| RNASEH2B | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 2 |
| RNASEH2C | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 3 |
| RNASET2 | Leukoencephalopathy, cystic, without megalencephaly |
| RNF168 | RIDDLE syndrome |
| RNF216 | Gordon Holmes syndrome |
| ROBO3 | Gaze palsy, familial horizontal, with progressive scoliosis, type 1 |
| ROGDI | Kohlschutter-Tonz syndrome |
| ROM1 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 7 digenic |
| ROR2 | Robinow syndrome, autosomal recessive |
| RORC | Immunodeficiency, type 42 |
| RP1 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 1 |
| RP2 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 2 X-linked |
| RPE65 | RPE65-related Leber congenital amaurosis/early-onset severe retinal dystrophy |
| RPGR | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 3 X-linked; Cone-rod dystrophy, X-linked, 1 |
| RPGRIP1 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 6 |
| RPGRIP1L | Joubert syndrome, type 7; Meckel syndrome, type 5; COACH syndrome |
| RPL10 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic 35 |
| RPS6KA3 | Coffin-Lowry syndrome |
| RRM2B | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, type 8A (encephalomyopathic type with renal tubulopathy) and type 8B (MNGIE type) |
| RS1 | Retinoschisis |
| RSPH1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 24 |
| RSPH3 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 32 |
| RSPH4A | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 11 |
| RSPH9 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 12 |
| RSPO4 | Anonychia congenita |
| RSPRY1 | Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Faden-Alkuraya type |
| RTEL1 | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive type 5 |
| RTN4IP1 | Optic atrophy 10 with or without ataxia, impaired intellectual development and seizures |
| RTTN | Microcephaly, short stature, and polymicrogyria with seizures |
| RUSC2 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 61 |
| RXYLT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A, 10 |
| RYR1 | RYR1 related congenitalmyopathy |
| S1PR2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 68 |
| SACS | Spastic ataxia, Charlevoix-Saguenay, type |
| SAG | Oguchi disease, type 1 |
| SAMD9 | Tumoral calcinosis, familial, normophosphatemic |
| SAMHD1 | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 5 |
| SAR1B | Chylomicron retention disease |
| SARS2 | Hyperuricemia, pulmonary hypertension, renal failure, and alkalosis |
| SBDS | Shwachman-Diamond syndrome |
| SBF1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4B3 |
| SBF2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4B2 |
| SC5D | Lathosterolosis |
| SCARB2 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 4 with or without renal failure |
| SCARF2 | Van den Ende-Gupta syndrome |
| SCN1B | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 52 |
| SCN4A | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 16 |
| SCN9A | Indifference to pain and autosomal recessive hereditary sensory neuropathy type 2D |
| SCNN1A | Pseudohypoaldosteronism, type 1 |
| SCNN1B | Pseudohypoaldosteronism, type 1 |
| SCNN1G | Pseudohypoaldosteronism, type 1 |
| SCO1 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 4 |
| SCO2 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| SCYL1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 21 |
| SDCCAG8 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 16 |
| SDHA | Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex II deficiency; Leigh syndrome |
| SDHAF1 | Mitochondrial complex II deficiency |
| SDR9C7 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 13 |
| SEC23A | Craniolenticulosutural dysplasia |
| SEC23B | Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital, type 2 |
| SEC24D | Cole-Carpenter syndrome 2 |
| SECISBP2 | Thyroid hormone metabolism, abnormal |
| SELENON | Multiminicore disease (rigid spine syndrome) |
| SEMA4A | Cone-rod dystrophy, type 10; Retinitis pigmentosa, type 35 |
| SEPSECS | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2D |
| SERAC1 | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria with deafness, encephalopathy, and Leigh-like syndrome (MEGDEL) |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency |
| SERPINB7 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, Nagashima type |
| SERPINB8 | Peeling skin syndrome 5 |
| SERPINC1 | Thrombophilia due to antithrombin III deficiency |
| SERPINE1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficiency |
| SERPINF1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 6 |
| SERPINF2 | Alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor deficiency |
| SERPING1 | Angioedema, hereditary, types 1 and 2 |
| SERPINH1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 10 |
| SETX | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| SFRP4 | Pyle disease |
| SFTPB | Surfactant metabolism dysfunction, pulmonary, type 1 |
| SFXN4 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 18 |
| SGCA | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 3 (LGMD R3) |
| SGCB | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 4 (LGMD R4) |
| SGCD | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 6 (LGMD R6) |
| SGCG | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 5 (LGMD R5) |
| SGPL1 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 14 |
| SGSH | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 3A (Sanfilippo A) |
| SH2D1A | Lymphoproliferative syndrome, X-linked, type 1 |
| SH3PXD2B | Frank-ter Haar syndrome |
| SH3TC2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4C |
| SI | Sucrase-isomaltase deficiency, congenital |
| SIL1 | Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome |
| SIX6 | Optic disc anomalies with retinal and/or macular dystrophy |
| SKIV2L | Trichohepatoenteric syndrome 2 |
| SLC10A2 | Bile acid malabsorption, primary |
| SLC11A2 | Anemia, hypochromic microcytic, with iron overload 1 |
| SLC12A1 | Bartter syndrome, type 1 |
| SLC12A3 | Gitelman syndrome |
| SLC12A5 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 34 |
| SLC12A6 | Agenesis of the corpus callosum with peripheral neuropathy |
| SLC13A5 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 25 |
| SLC16A1 | Monocarboxylate transporter 1 deficiency |
| SLC16A2 | Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome |
| SLC17A5 | Salla disease |
| SLC18A3 | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 21 presynaptic |
| SLC19A2 | Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome |
| SLC19A3 | Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome, type 2 (biotin- or thiamine-responsive encephalopathy type) |
| SLC1A1 | Dicarboxylic aminoaciduria |
| SLC1A4 | Spastic tetraplegia, thin corpus callosum, and progressive microcephaly |
| SLC22A12 | Hypouricemia, renal |
| SLC22A5 | Carnitine deficiency, systemic primary |
| SLC24A1 | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), type 1D, autosomal recessive |
| SLC24A4 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type IIA5 |
| SLC24A5 | Albinism, oculocutaneous, type 6 |
| SLC25A1 | Combined D-2- and L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria |
| SLC25A12 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 39 |
| SLC25A13 | Citrullinemia, type 2 neonatal-onset; Citrullinemia, type 2 adult-onset |
| SLC25A15 | Hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinemia syndrome |
| SLC25A19 | Microcephaly, Amish type; Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 4 (progressive polyneuropathy type) |
| SLC25A20 | Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency |
| SLC25A22 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 3 |
| SLC25A26 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 28 |
| SLC25A3 | Mitochondrial phosphate carrier deficiency |
| SLC25A38 | Anemia, sideroblastic, type 2 pyridoxine-refractory |
| SLC25A4 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, type 12B (cardiomyopathic type) AR |
| SLC25A46 | Neuropathy, hereditary motor and sensory, type VIB |
| SLC26A2 | Achondrogenesis, type 1B (diastrophic dysplasia) |
| SLC26A3 | Diarrhea 1 secretory chloride, congenital |
| SLC26A4 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 4; Pendred syndrome |
| SLC26A5 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 61 |
| SLC27A4 | Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome |
| SLC29A3 | Histiocytosis-lymphadenopathy plus syndrome |
| SLC2A1 | GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1, infantile onset, severe |
| SLC2A10 | Arterial tortuosity syndrome |
| SLC2A2 | Fanconi-Bickel syndrome |
| SLC2A9 | Hypouricemia, renal, type 2 |
| SLC30A10 | Hypermanganesemia with dystonia, type 1 |
| SLC33A1 | Congenital cataracts, hearing loss, and neurodegeneration |
| SLC34A1 | Hypercalcemia, infantile, type 2 |
| SLC34A2 | Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis |
| SLC34A3 | Hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria |
| SLC35A1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2F |
| SLC35A3 | Arthrogryposis, impaired intellectual development, and seizures |
| SLC35C1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2C |
| SLC35D1 | Schneckenbecken dysplasia |
| SLC37A4 | Glycogen storage disease, type 1B |
| SLC38A8 | Foveal hypoplasia 2 with or without optic nerve misrouting and/or anterior segment dysgenesis |
| SLC39A13 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, spondylodysplastic type, 3 |
| SLC39A14 | Hypermanganesemia with dystonia 2 |
| SLC39A4 | Acrodermatitis enteropathica |
| SLC39A8 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type IIn |
| SLC3A1 | Cystinuria |
| SLC45A1 | Intellectual developmental disorder with neuropsychiatric features |
| SLC45A2 | Albinism, oculocutaneous, type 4 |
| SLC46A1 | Folate malabsorption, hereditary |
| SLC4A1 | Distal renal tubular acidosis |
| SLC4A11 | Corneal endothelial dystrophy, autosomal recessive |
| SLC4A4 | Renal tubular acidosis, proximal, with ocular abnormalities |
| SLC52A2 | Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome, type 2 |
| SLC52A3 | Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome, type 1 |
| SLC5A1 | Glucose/galactose malabsorption |
| SLC5A2 | Renal glucosuria |
| SLC5A5 | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis, type 1 |
| SLC5A7 | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 20 presynaptic |
| SLC6A17 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 48 |
| SLC6A19 | Hartnup disorder |
| SLC6A3 | Parkinsonism-dystonia, infantile |
| SLC6A5 | Hyperekplexia, type 3 |
| SLC6A8 | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome, type 1 |
| SLC6A9 | Glycine encephalopathy with normal serum glycine |
| SLC7A14 | Retinitis pigmentosa 68 |
| SLC7A7 | Lysinuric protein intolerance |
| SLC7A9 | Cystinuria |
| SLC9A3 | Diarrhea 8 secretory sodium, congenital |
| SLC9A6 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Christianson type |
| SLCO2A1 | Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, primary, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| SLITRK6 | Deafness and myopia |
| SLURP1 | Meleda disease |
| SLX4 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group P |
| SMARCAL1 | Schimke immunoosseous dysplasia |
| SMARCD2 | Specific granule deficiency 2 |
| SMG9 | Heart and brain malformation syndrome |
| SMN1 | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| SMN2 | {Spinal muscular atrophy, type III, modifier of} |
| SMOC1 | Microphthalmia. with limb anomalies |
| SMOC2 | Dentin dysplasia, type 1 with microdontia and misshapen teeth |
| SMPD1 | Niemann-Pick disease, type A; Niemann-Pick disease, type B |
| SMS | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Snyder-Robinson type |
| SNAP29 | Cerebral dysgenesis, neuropathy, ichthyosis, and palmoplantar keratoderma syndrome |
| SNX10 | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive, type 8 |
| SNX14 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 20 |
| SOBP | Impaired intellectual development, anterior maxillary protrusion, and strabismus |
| SOD1 | Spastic tetraplegia and axial hypotonia, progressive; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, type 1 |
| SOHLH1 | Ovarian dysgenesis 5 |
| SOST | Sclerosteosis, type 1; Van Buchem disease |
| SOX18 | Hypotrichosis-lymphedema-telangiectasia syndrome |
| SOX3 | Panhypopituitarism, X-linked |
| SP110 | Hepatic venoocclusive disease with immunodeficiency |
| SP7 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type XII |
| SPAG1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 28 |
| SPARC | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type XVII |
| SPART | Spactic paraplegia, type 20 autosomal recessive |
| SPATA5 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with hearing loss, seizures, and brain abnormalities |
| SPATA7 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 3 |
| SPEG | Centronuclear myopathy, type 5 |
| SPG11 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, type 5 juvenile |
| SPG21 | Mast syndrome |
| SPG7 | Spastic paraplegia, type 7 autosomal recessive |
| SPINK1 | Tropical calcific pancreatitis |
| SPINK5 | Netherton syndrome |
| SPINT2 | Diarrhea 3 secretory sodium, congenital, syndromic |
| SPR | Dystonia, dopa-responsive, due to sepiapterin reductase deficiency |
| SPRTN | Ruijs-Aalfs syndrome |
| SPTA1 | Pyropoikilocytosis; Apherocytosis, type 3 |
| SPTBN2 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 14 |
| SPTBN4 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with hypotonia, neuropathy, and deafness |
| SQSTM1 | Neurodegeneration with ataxia, dystonia, and gaze palsy, childhood-onset |
| SRD5A2 | 46,XY disorder of sex development due to 5-alpha-reductase 2 deficiency (pseudovaginal perineoscrotal hypospadias) |
| SRD5A3 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1Q; Kahrizi syndrome |
| SRPX2 | Rolandic epilepsy, impaired intellectual development, and speech dyspraxia |
| ST14 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 11 |
| ST3GAL3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 12; Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 15 |
| ST3GAL5 | Salt and pepper developmental regression syndrome |
| STAC3 | Native American myopathy |
| STAG3 | Premature ovarian failure 8 |
| STAMBP | Microcephaly-capillary malformation syndrome |
| STAR | Lipoid adrenal hyperplasia |
| STAT1 | Immunodeficiency, type 31B, mycobacterial and viral infections |
| STAT2 | Immunodeficiency, type 44 |
| STAT5B | Laron syndrome with immunodeficiency |
| STIL | Microcephaly, type 7 primary, autosomal recessive |
| STIM1 | Immunodeficiency, type 10 |
| STK4 | T-cell immunodeficiency, recurrent infections, autoimmunity, and cardiac malformations |
| STRA6 | Microphthalmia, isolated, with coloboma, type 8 |
| STRADA | Polyhydramnios, megalencephaly, and symptomatic epilepsy |
| STRC | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 16 |
| STUB1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 16 |
| STX11 | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, familial, type 4 |
| STXBP2 | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, familial, type 5 |
| SUCLA2 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, type 5 (encephalomyopathic with or without methylmalonic aciduria) |
| SUCLG1 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, type 9 (encephalomyopathic, type with methylmalonic aciduria) |
| SUFU | Joubert syndrome, type 32 |
| SUGCT | Glutaric aciduria, type 3 |
| SULT2B1 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 14 |
| SUMF1 | Multiple sulfatase deficiency |
| SUN5 | Spermatogenic failure, type 16 |
| SUOX | Sulfite oxidase deficiency |
| SURF1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4K; Leigh syndrome, due to COX IV deficiency |
| SYN1 | Epilepsy, X-linked, with variable learning disabilities and behavior disorders |
| SYNE1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 8 |
| SYNE4 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 76 |
| SYNJ1 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 53 |
| SYP | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 96 |
| SYT14 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 11 |
| SZT2 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 18 |
| TAC3 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 10 with or without anosmia |
| TACO1 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 8 |
| TACR3 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 11 with or without anosmia |
| TACSTD2 | Corneal dystrophy, gelatinous drop-like |
| TAF1 | Dystonia-Parkinsonism, X-linked |
| TAF13 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 60 |
| TAF2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 40 |
| TAF6 | Alazami-Yuan syndrome |
| TALDO1 | Transaldolase deficiency |
| TANGO2 | Metabolic encephalomyopathic crises, recurrent, with rhabdomyolysis, cardiac arrhythmias, and neurodegeneration |
| TAP1 | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 1 |
| TAP2 | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 1 due to TAP2 deficiency |
| TAPBP | Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type 1 |
| TAPT1 | Osteochondrodysplasia, complex lethal, Symoens-Barnes-Gistelinck type |
| TAT | Tyrosinemia, type 2 |
| TAZ | Barth syndrome |
| TBC1D20 | Warburg micro syndrome 4 |
| TBC1D23 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 11 |
| TBC1D24 | DOORS (deafness, onychodystrophy, osteodystrophy, impaired intellectual development, and seizures) syndrome; Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 16; Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 86 |
| TBC1D7 | Macrocephaly/megalencephaly syndrome, autosomal recessive |
| TBCD | Encephalopathy, progressive, early-onset, with brain atrophy and thin corpus callosum |
| TBCE | Encephalopathy, progressive, with amyotrophy and optic atrophy; Hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism syndrome; Kenny-Caffey syndrome, type 1 |
| TBCK | Hypotonia, infantile, with psychomotor retardation and characteristic facies 3 |
| TBX15 | Cousin syndrome |
| TBX19 | Congenital isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency |
| TBXAS1 | Ghosal syndrome |
| TCAP | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 7 (LGMD R7) |
| TCIRG1 | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| TCN2 | Transcobalamin II deficiency |
| TCTN1 | Joubert syndrome, type 13 |
| TCTN2 | Joubert syndrome, type 24; ?Meckel syndrome, type 8 |
| TCTN3 | Joubert syndrome 18 |
| TDP1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive with axonal neuropathy |
| TDP2 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 23 |
| TDRD7 | Cataract 36 |
| TECPR2 | Spastic paraplegia, type 49 autosomal recessive |
| TECR | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 14 |
| TECRL | Ventricular tachycardia, catecholaminergic polymorphic, 3 |
| TECTA | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 21 |
| TELO2 | You-Hoover-Fong syndrome |
| TENM3 | Microphthalmia, isolated, with coloboma 9 |
| TERT | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive, type 4 |
| TEX15 | Spermatogenic failure, type 25 |
| TF | Atransferrinemia |
| TFR2 | Hemochromatosis, type 3 |
| TFRC | Immunodeficiency, type 46 |
| TG | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis, type 3 |
| TGDS | Catel-Manzke syndrome |
| TGM1 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| TGM5 | Peeling skin syndrome, type 2 |
| TH | Segawa syndrome, recessive |
| THOC2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 12 |
| THOC6 | Beaulieu-Boycott-Innes syndrome |
| THRB | Thyroid hormone resistance, autosomal recessive |
| TIMM50 | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 9 |
| TIMM8A | Mohr-Tranebjaerg syndrome |
| TIMMDC1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 31 |
| TJP2 | Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, type 4 |
| TK2 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome , type 2 (myopathic type) |
| TKT | Short stature, developmental delay, and congenital heart defects |
| TLE6 | Preimplantation embryonic lethality |
| TMC1 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 7 |
| TMC6 | Epidermodysplasia verruciformis |
| TMC8 | Epidermodysplasia verruciformis |
| TMCO1 | Craniofacial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and impaired intellectual development 1 |
| TMEM107 | Meckel syndrome, type 13; Orofaciodigital syndrome, type 16 |
| TMEM126A | Optic atrophy 7 |
| TMEM126B | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 29 |
| TMEM138 | Joubert syndrome 16 |
| TMEM165 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2K |
| TMEM199 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2P |
| TMEM216 | Joubert syndrome, type 2; Meckel syndrome, type 2 |
| TMEM231 | Joubert syndrome, type 20; Meckel syndrome,type 11 |
| TMEM237 | Joubert syndrome, type 14 |
| TMEM260 | Structural heart defects and renal anomalies syndrome |
| TMEM38B | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type XIV |
| TMEM67 | Joubert syndrome, type 6; Meckel syndrome, type 3; COACH syndrome |
| TMEM70 | Mitochondrial complex V (ATP synthase) deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| TMIE | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 6 |
| TMPRSS15 | Enterokinase deficiency |
| TMPRSS3 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 45573 |
| TMPRSS6 | Iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia |
| TMTC3 | Lissencephaly 8 |
| TNFRSF11A | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive, type 7 |
| TNFRSF11B | Paget disease of bone, type 5 juvenile-onset |
| TNFRSF13B | Immunodeficiency, common variable, type 2 |
| TNFSF11 | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| TNIK | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 54 |
| TNNT1 | Nemaline myopathy , type 5 Amish type |
| TNXB | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classic-like |
| TOE1 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 7 |
| TOP3A | Microcephaly, growth restriction, and increased sister chromatid exchange 2 |
| TP53RK | Galloway-Mowat syndrome 4 |
| TPI1 | Hemolytic anemia due to triosephosphate isomerase deficiency |
| TPK1 | Episodic encephalopathy due to thiamine pyrophosphokinase deficiency |
| TPM3 | Nemaline myopathy, type 1; Congenital fiber-type disproportion myopathy |
| TPO | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis, type 2A |
| TPP1 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 2; Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 7 |
| TPRN | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 79 |
| TRAF3IP1 | Senior-Loken syndrome, type 9 |
| TRAIP | Seckel syndrome, type 9 |
| TRAPPC11 | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 18 (LGMD R18) |
| TRAPPC12 | Encephalopathy, progressive, early-onset, with brain atrophy and spasticity |
| TRAPPC6B | Neurodevelopmental disorder with microcephaly, epilepsy, and brain atrophy |
| TRAPPC9 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 13 |
| TRDN | Ventricular tachycardia, catecholaminergic polymorphic, type 5 with or without muscle weakness |
| TREM2 | Nasu-Hakola disease |
| TREX1 | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 1 |
| TRHR | Hypothyroidism, congenital, nongoitrous, type 7 |
| TRIM2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 2R |
| TRIM32 | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 8 (LGMD R8) |
| TRIM37 | Mulibrey nanism |
| TRIOBP | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 28 |
| TRIP11 | Achondrogenesis, type 1A |
| TRIP13 | Mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome 3 |
| TRIP4 | Spinal muscular atrophy with congenital bone fractures 1 |
| TRIT1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 35 |
| TRMT10A | Microcephaly, short stature, and impaired glucose metabolism 1 |
| TRMT10C | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 30 |
| TRMT5 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 26 |
| TRMU | Liver failure, transient infantile |
| TRNT1 | Retinitis pigmentosa and erythrocytic microcytosis |
| TRPM1 | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), type 1C, autosomal recessive |
| TRPM6 | Familial hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia |
| TRPV6 | Hyperparathyroidism, transient neonatal |
| TSEN15 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2F |
| TSEN2 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2B |
| TSEN34 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2C |
| TSEN54 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2A; Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 4 |
| TSFM | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency, type 3 |
| TSHB | Hypothyroidism, congenital, nongoitrous, type 4 |
| TSHR | Hypothyroidism, congenital, nongoitrous, type 1 |
| TSPAN7 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 58 |
| TSPYL1 | Sudden infant death with dysgenesis of the testes syndrome |
| TTC19 | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| TTC21B | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia, type 4 with or without polydactyly |
| TTC37 | Trichohepatoenteric syndrome 1 |
| TTC7A | Gastrointestinal defects and immunodeficiency syndrome |
| TTC8 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 8 |
| TTI2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 39 |
| TTLL5 | Cone-rod dystrophy 19 |
| TTN | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 10 (LGMDR10); Early-onset myopathy with fatal cardiomyopathy (Salih myopathy) |
| TTPA | Ataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency |
| TUBA8 | Cortical dysplasia, complex, with other brain malformations, type 8 |
| TUBGCP4 | Microcephaly and chorioretinopathy, autosomal recessive, type 3 |
| TUBGCP6 | Microcephaly and chorioretinopathy, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| TUFM | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 4 |
| TULP1 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 15 |
| TUSC3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 7 |
| TWIST2 | Focal facial dermal dysplasia, type 3 (Setleis type) |
| TWNK | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, type 7 (hepatocerebral type); Perrault syndrome type 5 |
| TXNL4A | Burn-McKeown syndrome |
| TYK2 | Immunodeficiency, type 35 |
| TYMP | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, type 1 (MNGIE type) |
| TYR | Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) type 1A; OCA type 1B |
| TYROBP | Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy, type 1 (Nasu-Hakola disease) |
| TYRP1 | Albinism, oculocutaneous, type 3 |
| UBA1 | Spinal muscular atrophy, X-linked 2, infantile |
| UBA5 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 44 |
| UBE2A | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Nascimento type |
| UBE2T | Fanconi anemia, complementation group T |
| UBE3A | Angelman syndrome |
| UBE3B | Kaufman oculocerebrofacial syndrome |
| UBR1 | Johanson-Blizzard syndrome |
| UCHL1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 79 autosomal recessive |
| UFM1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 14 |
| UGT1A1 | Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type 1; Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type 2 |
| UMPS | Orotic aciduria |
| UNC13D | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, familial, type 3 |
| UNC80 | Hypotonia, infantile, with psychomotor retardation and characteristic facies, type 2 |
| UNG | Immunodeficiency with hyper IgM, type 5 |
| UPB1 | Beta-ureidopropionase deficiency |
| UPF3B | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic 14 |
| UQCRB | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear, type 3 |
| UQCRC2 | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 5 |
| UQCRQ | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear, type 4 |
| UROD | Porphyria cutanea tarda |
| UROS | Porphyria, congenital erythropoietic |
| USB1 | Poikiloderma with neutropenia |
| USH1C | Usher syndrome, type 1C; Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 18A |
| USH1G | Usher syndrome, type 1G |
| USH2A | Usher syndrome, type 2A |
| USP18 | Pseudo-TORCH syndrome 2 |
| USP9X | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 99 |
| UVSSA | UV-sensitive syndrome, type 3 |
| VAC14 | Striatonigral degeneration, childhood-onset |
| VARS1 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with microcephaly, seizures, and cortical atrophy |
| VARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 20 |
| VDR | Rickets, vitamin D-resistant, type 2A |
| VIPAS39 | Arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction and cholestasis, type 2 |
| VKORC1 | Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, combined deficiency of, type 2 |
| VLDLR | Cerebellar hypoplasia, impaired intellectual development, and dysequilibrium syndrome 1 |
| VPS13A | Choreoacanthocytosis |
| VPS13B | Cohen syndrome |
| VPS13C | Parkinson disease 23 autosomal recessive, early onset |
| VPS33B | Arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction and cholestasis, type 1 |
| VPS37A | Spastic paraplegia, type 53 autosomal recessive |
| VPS45 | Neutropenia, severe congenital, type 5 |
| VPS53 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2E |
| VRK1 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 1A |
| VSX2 | Microphthalmia with coloboma 3; Isolated microphthalmia 2 |
| VWF | von Willibrand disease, type 3 |
| WARS2 | Neurodevelopmental disorder, mitochondrial, with abnormal movements and lactic acidosis, with or without seizures |
| WAS | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; Thrombocytopenia, X-linked |
| WASHC4 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 43 |
| WASHC5 | Ritscher-Schinzel syndrome, type 1 |
| WDR19 | Nephronophthisis, type 13; Senior-Loken syndrome, type 8 |
| WDR35 | Cranioectodermal dysplasia 2 |
| WDR45B | Neurodevelopmental disorder with spastic quadriplegia and brain abnormalities with or without seizures |
| WDR62 | Microcephaly, type 2 primary, autosomal recessive, with or without cortical malformations |
| WDR72 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type 2A3 (hypomaturation type) |
| WDR73 | Galloway-Mowat syndrome 1 |
| WDR81 | Cerebellar ataxia, impaired intellectual development, and dysequilibrium syndrome, type 2; Hydrocephalus, congenital, 3, with brain anomalies |
| WEE2 | Oocyte maturation defect 5 |
| WFS1 | Wolfram syndrome, type 1 |
| WHRN | Usher syndrome, type 2D; Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 31 |
| WIPF1 | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome 2 |
| WNK1 | Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, type 2 |
| WNT1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type XV |
| WNT10A | Ectodermal dysplasia 16 (odontoonychodermal dysplasia) |
| WNT10B | Split-hand/foot malformation, type 6 |
| WNT3 | Tetra-amelia syndrome |
| WNT7A | Fuhrmann syndrome |
| WRAP53 | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive, type 3 |
| WRN | Werner syndrome |
| WWOX | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 28; Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 12 |
| XDH | Xanthinuria, type 1 |
| XIAP | Lymphoproliferative syndrome, X-linked, 2 |
| XPA | Xeroderma pigmentosum, group A |
| XPC | Xeroderma pigmentosum, group C |
| XPNPEP3 | Nephronophthisis-like nephropathy, type 1 |
| XRCC4 | Short stature, microcephaly, and endocrine dysfunction |
| XYLT1 | Desbuquois dysplasia, type 2 |
| XYLT2 | Spondyloocular syndrome |
| YARS2 | Myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia, type 2 |
| YY1AP1 | Grange syndrome |
| ZAP70 | Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, type 2; Immunodeficiency, type 48 |
| ZBTB24 | Immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies syndrome, type 2 |
| ZC3H14 | intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive, type 56 |
| ZDHHC9 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Raymond type |
| ZFYVE26 | Spastic paraplegia, type 15 autosomal recessive |
| ZMPSTE24 | Mandibuloacral dysplasia with, type B lipodystrophy |
| ZMYND10 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 22 |
| ZNF408 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 72 |
| ZNF423 | Joubert syndrome, type 19 |
| ZNF469 | Brittle cornea syndrome, type 1 |
| ZNF711 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 97 |
| ZNHIT3 | PEHO syndrome |
| ZP1 | Oocyte maturation defect, type 1 |
Spisak bolesti koje analizira

PLUS
| ACADM | Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| AGXT | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 1 |
| ARSA | Metachromatic leukodystrophy |
| ATP7B | Wilson disease |
| BTD | Biotinidase deficiency |
| CBS | Homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis |
| DHCR7 | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome |
| EMD | Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, type 1 X-linked |
| FMR1 | Fragile X syndrome |
| GAA | Glycogen storage disease, type 2 |
| GALC | Krabbe disease |
| GALT | Galactosemia |
| GBA | Gaucher Disease |
| GJB1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, X-linked dominant, type 1 |
| GJB2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 1A; Deafness, digenic, GJB2/GJB6 |
| GJB6 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 1B; Deafness, digenic GJB2/GJB6 |
| GLA | Fabry disease |
| HADHA | Long-chain 3-hydroxyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency; Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency |
| HBA1 | Alpha-thalassemia |
| HBA2 | Alpha-thalassemia |
| HBB | Beta-thalassemia, Sickle hemoglobinopathies cell anemia and other HBB-related |
| HEXA | Tay-Sachs disease |
| MEFV | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| MMACHC | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblC type |
| PAH | Phenylketonuria |
| PMM2 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1A |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency |
| SLC26A2 | Achondrogenesis, type 1B (diastrophic dysplasia) |
| SMN1 | Spinal muscular atrophy |
Spisak bolesti koje analizira

ADVANCE
| AAAS | Triple-A syndrome (achalasia-addisonianism-alacrimia) |
| ABAT | GABA-transaminase deficiency |
| ABCA12 | Ichthyosis congenital autosomal recessive type 4A and 4B (harlequin) |
| ABCA3 | Surfactant metabolism dysfunction, pulmonary, type 3 |
| ABCC8 | Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, type 1 (congenital hyperinsulinism); Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) |
| ABCD1 | Adrenoleukodystrophy |
| ABHD12 | PHARC syndrome (polyneuropathy, hearing loss, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa and cataract) |
| ACAD9 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase 9 deficiency (mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear, type 20) |
| ACADM | Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ACADS | Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ACADVL | Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficiency |
| ACAT1 | Alpha-methylacetoacetic aciduria (3-ketothiolase deficiency) |
| ACE | Renal tubular dysgenesis |
| ACOX1 | Peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase deficiency |
| ACTA1 | Nemaline myopathy 3; Congenital fiber-type disproportion myopathy 1 |
| ADA | Severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA) |
| ADAMTS10 | Weill-Marchesani syndrome, type 1 recessive |
| ADAMTS13 | Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, familial (Schulman-Upshaw syndrome) |
| AFF2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 109 |
| AGA | Aspartylglucosaminuria (glycosylasparaginase deficiency) |
| AGL | Glycogen storage disease, type 3 |
| AGPAT2 | Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (Berardinelli-Seip syndrome) |
| AGPS | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 3 |
| AGRN | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 8 |
| AGXT | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 1 |
| AHI1 | Joubert syndrome, type 3 |
| AIMP1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 3 |
| AIRE | Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome, type 1 |
| ALDH18A1 | Spastic paraplegia, type 9B, autosomal recessive; Cutis laxa, type 3A (De Barsy syndrome) |
| ALDH3A2 | Sjogren-Larsson syndrome |
| ALDH5A1 | Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ALDH7A1 | Epilepsy, pyridoxine-dependent |
| ALDOB | Fructose intolerance, hereditary |
| ALG12 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1G |
| ALG6 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1C |
| ALMS1 | Alström syndrome |
| ALOX12B | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| ALPL | Hypophosphatasia, infantile/childhood |
| AMACR | Bile acid synthesis defect, congenital, type 4; Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase deficiency |
| AMT | Glycine encephalopathy |
| ANO10 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 10 |
| ANTXR2 | Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome |
| AP1S2 | Pettigrew syndrome |
| APTX | Ataxia, early-onset, with oculomotor apraxia and hypoalbuminemia |
| AQP2 | Diabetes insipidus, nephrogenic, type 2 |
| ARFGEF2 | Periventricular heterotopia with microcephaly |
| ARL13B | Joubert syndrome type 8 |
| ARL6 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 3 |
| ARSA | Metachromatic leukodystrophy |
| ARSB | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 6 (Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome) |
| ARSE | Chondrodysplasia punctata, X-linked recessive |
| ARX | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, type 1; ARX-related developmental disorders |
| ASL | Argininosuccinic aciduria |
| ASPA | Canavan disease |
| ASPM | Primary microcephaly type 5 autosomal recessive |
| ASS1 | Citrullinemia, type 1 |
| ATM | Ataxia-telangiectasia |
| ATP6V0A2 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 2A; Wrinkly skin syndrome |
| ATP7A | Menkes disease; Occipital horn syndrome |
| ATP7B | Wilson disease |
| ATR | Seckel syndrome, type 1 |
| ATRX | Intellectual disability-hypotonic facies syndrome, X-linked; Alpha-thalassemia/intellectual developmental disorder syndrome |
| AUH | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type 1 |
| BBS1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 1 |
| BBS10 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 10 |
| BBS12 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 12 |
| BBS2 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 2 |
| BBS7 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 7 |
| BBS9 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 9 |
| BCKDHA | Maple syrup urine disease, type 1A |
| BCKDHB | Maple syrup urine disease, type 1B |
| BCS1L | Mitochondrial complex III deficiency nuclear type 1; GRACILE syndrome; Bjornstad syndrome |
| BEST1 | Bestrophinopathy, AR |
| BLM | Bloom syndrome |
| BRWD3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 93 |
| BSCL2 | Congenital generalized lipodystrophy, type 2; Encephalopathy, progressive, with or without lipodystrophy |
| BTD | Biotinidase deficiency |
| BUB1B | Mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome 1 |
| CBS | Homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase |
| CC2D2A | Joubert syndrome, type 9; Meckel syndrome, type 6; COACH syndrome, 2 |
| CCDC88C | Hydrocephalus, congenital, type 1 |
| CD40LG | Hyper-IgM syndrome, type 1 (immunodeficiency, X-linked, with hyper-IgM, type 1) |
| CDAN1 | Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital, type 1A |
| CDH23 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 12; Usher syndrome, type 1D |
| CDK5RAP2 | Primary microcephaly type 3 autosomal recessive |
| CENPJ | Primary microcephaly type 6 autosomal recessive |
| CEP152 | Primary microcephaly type 9 autosomal recessive |
| CEP290 | Meckel syndrome, type 4; Joubert syndrome, type 5; Leber congenital amaurosis, type 10 |
| CFL2 | Nemaline myopathy, type 7 autosomal recessive |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis |
| CHAT | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 6 presynaptic |
| CHM | Choroideremia |
| CHRND | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 3B, fast-channel; Multiple pterygium syndrome, lethal type |
| CHRNE | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 4B, fast-channel; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 4C, associated with acetylcholine receptor deficiency |
| CHRNG | Multiple pterygium syndrome (MPS), Escobar type; MPS, lethal type |
| CHST14 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, musculocontractural, type 1 |
| CHST3 | Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia with congenital joint dislocations |
| CLCN1 | Myotonia congenita, recessive |
| CLN3 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 3 |
| CLN5 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 5 |
| CLN6 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 6 |
| CLN8 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 8 |
| CLRN1 | Usher syndrome, type 3A |
| CNGB3 | Achromatopsia, type 3 |
| COG4 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2J |
| COL11A2 | Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia, autosomal recessive |
| COL17A1 | Epidermolysis bullosa, junctional, non-Herlitz type |
| COL4A3 | Alport syndrome, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| COL4A5 | Alport syndrome, X-linked |
| COL7A1 | Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB), Hallopeau-Siemens (HS) type and non-HS type; DEB pruriginosa; DEB pretibial |
| COLQ | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 5 |
| COQ2 | Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency, type 1 |
| CORO1A | Immunodeficiency, type 8 |
| CPS1 | Carbamoylphosphate synthetase 1 deficiency |
| CPT1A | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type 1A deficiency, hepatic |
| CPT2 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type 2 deficiency, lethal neonatal; Carnitine palmitoyltransferase type 2 deficiency, infantile |
| CRLF1 | Cold-induced sweating syndrome type 1 |
| CRTAP | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type 7 |
| CSTB | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic type 1A (Unverricht and Lundborg) |
| CTC1 | Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts |
| CTNS | Nephropathic cystinosis |
| CTSD | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 10 |
| CTSK | Pycnodysostosis |
| CUL4B | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Cabezas type |
| CUL7 | 3M syndrome 1 |
| CYBB | Chronic granulomatous disease, X-linked |
| CYP11A1 | 46,XY disorder of sex development-adrenal insufficiency due to CYP11A1 deficiency |
| CYP1B1 | Glaucoma, primary congenital, type 3A |
| CYP21A2 | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency |
| CYP27A1 | Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis |
| CYP27B1 | Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type 1 |
| D2HGDH | D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria |
| DBH | Dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency |
| DBT | Maple syrup urine disease, type 2 |
| DCLRE1C | Omenn syndrome; Severe combined immunodeficiency, Athabascan type |
| DCX | Lissencephaly, X-linked, type 1 |
| DDC | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency |
| DGUOK | DGUOK-related mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome |
| DHCR7 | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome |
| DHDDS | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 59 |
| DHH | 46,XY complete gonadal dysgenesis |
| DLAT | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 deficiency |
| DLG3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 90 |
| DMD | Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy |
| DMD | Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy |
| DMP1 | Hypophosphatemic rickets, autosomal recessive |
| DNAH11 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 7 with or without situs inversus |
| DNAH5 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 3 with or without situs inversus |
| DNAL1 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, type 16 |
| DOCK8 | Hyper-IgE recurrent infection syndrome, autosomal recessive |
| DOK7 | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, type 3; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 10 |
| DPAGT1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1J; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 13 |
| DPYD | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency |
| DYNC2H1 | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia, type 3 with or without polydactyly |
| EDA | Ectodermal dysplasia, type 1 hypohidrotic, X-linked |
| EDNRB | ABCD syndrome |
| EIF2AK3 | Wolcott-Rallison syndrome |
| EIF2B2 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B3 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B4 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EIF2B5 | Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter (VWM) |
| EMD | Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, type 1 X-linked |
| ENPP1 | Arterial calcification, generalized, of infancy, type 1 |
| EPG5 | Vici syndrome |
| EPM2A | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 2A (Lafora) |
| ERCC2 | Trichothiodystrophy, type 1 |
| ERCC4 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group Q |
| ERCC5 | Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome, type 3 |
| ERCC6 | Cockayne syndrome, type B; Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome, type 1 |
| ERCC8 | Cockayne syndrome, type A |
| ESCO2 | Roberts syndrome; Juberg-Hayward syndrome |
| ETFDH | Glutaric acidemia, type 2C |
| ETHE1 | Ethylmalonic encephalopathy |
| EVC | Ellis-van Creveld syndrome |
| EVC2 | Ellis-van Creveld syndrome |
| EXOSC3 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 1B |
| F11 | Factor XI deficiency |
| F8 | Hemophilia A |
| F9 | Hemophilia B |
| FA2H | Spastic paraplegia, type 35 autosomal recessive |
| FAH | Tyrosinemia, type 1 |
| FAM20C | Raine syndrome |
| FANCA | Fanconi anemia, complementation group A |
| FANCC | Fanconi anemia, complementation group C |
| FANCF | Fanconi anemia, complementation group F |
| FANCG | Fanconi anemia, complementation group G |
| FANCI | Fanconi anemia, complementation group I |
| FGD1 | Aarskog-Scott syndrome; intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, type 16 |
| FKRP | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 5A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 5B; Type 5C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 9 [LGMDR9]) |
| FKTN | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 4A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 4B; Type 4C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 13 [LGMD R13]) |
| FMO3 | Trimethylaminuria |
| FMR1 | Fragile X syndrome |
| FRAS1 | Fraser syndrome, type 1 |
| FTSJ1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 9 |
| FUCA1 | Fucosidosis |
| G6PC | Glycogen storage disease, type 1A |
| G6PD | Hemolytic anemia, G6PD deficient (favism) |
| GAA | Glycogen storage disease, type 2 |
| GALC | Krabbe disease |
| GALT | Galactosemia |
| GAMT | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome, type 2 |
| GAN | Giant axonal neuropathy, type 1 |
| GATM | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome, type 3 |
| GBA | Gaucher Disease |
| GBE1 | Glycogen storage disease, type 4 |
| GCDH | Glutaricaciduria, type 1 |
| GFM1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency, type 1 |
| GFPT1 | Myasthenia, congenital, type 12 with tubular aggregates |
| GJB1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, X-linked dominant, type 1 |
| GJB2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 1A; Deafness, digenic, GJB2/GJB6 |
| GJB6 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 1B; Deafness, digenic GJB2/GJB6 |
| GLA | Fabry disease |
| GLB1 | GM1-gangliosidosis, types 1-3; Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 4B (Morquio) |
| GLDC | Glycine encephalopathy |
| GLRA1 | Hyperekplexia, type 1 |
| GNPTAB | Mucolipidosis 2 alpha/beta; Mucolipidosis 3 alpha/beta |
| GNRHR | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, type 7 without anosmia |
| GOSR2 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 6 |
| GP1BA | Bernard-Soulier syndrome, type A1 |
| GP1BB | Bernard-Soulier syndrome, type B |
| GPHN | Molybdenum cofactor deficiency C |
| GPR143 | Ocular albinism, type 1 (Nettleship-Falls type) |
| GRHPR | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 2 |
| GRIP1 | Fraser syndrome 3 |
| HADH | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| HADHA | Long-chain 3-hydroxyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency; Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency |
| HBA1 | Alpha-thalassemia |
| HBA2 | Alpha-thalassemia |
| HBB | Beta-thalassemia, Sickle cell anemia and other HBB-related hemoglobinopathies |
| HEXA | Tay-Sachs disease |
| HEXB | Sandhoff disease, infantile, juvenile, and adult forms |
| HGSNAT | Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3C (Sanfilippo syndrome C) |
| HIBCH | 3-hydroxyisobutryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency |
| HLCS | Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency |
| HPS3 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 3 |
| HPS4 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 4 |
| HPS6 | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 6 |
| HSD17B3 | 46,XY disorder of sex development due to 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3 deficiency |
| HSD17B4 | D-bifunctional protein deficiency |
| HSD3B2 | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency |
| HSPG2 | Dyssegmental dysplasia, Silverman-Handmaker type |
| IDS | Mucopolysaccharidosis, type 2 |
| IDUA | Mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 |
| IGHMBP2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2S |
| IL1RAPL1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 21 |
| IL2RG | Severe combined immunodeficiency, X-linked |
| IL7R | Severe combined immunodeficiency, T-cell negative, B-cell/natural killer cell-positive type |
| INPP5E | Joubert syndrome, type 1 |
| INSR | Diabetes mellitus, insulin-resistant, with acanthosis nigricans, type A |
| ITGB4 | Epidermolysis bullosa, junctional, with pyloric atresia |
| IVD | Isovaleric acidemia |
| JAK3 | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, autosomal recessive, T-negative/B-positive type |
| KCNJ1 | Bartter syndrome, type 2 |
| KCNJ13 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 16 |
| KCTD7 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 3 with or without intracellular inclusions |
| KDM5C | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Claes-Jensen type |
| KIF7 | Acrocallosal syndrome; Joubert syndrome, type 12 |
| L1CAM | L1 Syndrome |
| LAMA2 | LAMA2-related muscular dystrophy |
| LAMA3 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type; JEB non-Herlitz type |
| LAMB2 | Pierson syndrome; Nephrotic syndrome, type 5 with or without ocular abnormalities |
| LAMB3 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type; JEB non-Herlitz type |
| LAMC2 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type; JEB non-Herlitz type |
| LIFR | Stuve-Wiedemann syndrome / Schwartz-Jampel type 2 syndrome |
| LMNA | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1A |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase deficiency |
| LRP2 | Donnai-Barrow syndrome |
| LRPPRC | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 5, (French-Canadian) |
| LTBP4 | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type 1C |
| MAN2B1 | Alpha-mannosidosis |
| MCCC2 | 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency, type 2 |
| MCOLN1 | Mucolipidosis type 4 |
| MCPH1 | Microcephaly type 1 primary, autosomal recessive |
| MFN2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2A2B |
| MFSD8 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 7 |
| MID1 | Opitz GBBB syndrome, type 1 |
| MKS1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 13; Meckel syndrome, type 1; Joubert syndrome, type 28 |
| MLC1 | Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts |
| MMAB | Methylmalonic aciduria, vitamin B12-responsive, type cblB |
| MMACHC | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblC type |
| MMADHC | Homocystinuria, cblD type, variant 1 |
| MMUT | Methylmalonic aciduria, mut(0) type |
| MPDU1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1F |
| MPI | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1B |
| MPV17 | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome type 6 (hepatocerebral); Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2EE |
| MPZ | Dejerine-Sottas disease |
| MTHFR | Homocystinuria due to MTHFR deficiency |
| MTM1 | Myotubular myopathy, X-linked |
| MTO1 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 10 |
| MTR | Homocystinuria-megaloblastic anemia, cblG complementation type |
| MUSK | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, type 1; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 9 associated with acetylcholine receptor deficiency |
| MVK | Mevalonic aciduria |
| MYO15A | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 3 |
| MYO5A | Griscelli syndrome, type 1 |
| MYO5B | Microvillus inclusion disease |
| MYO7A | Usher syndrome, type 1B; Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 2 |
| NAGA | Schindler disease, type I |
| NBN | Nijmegen breakage syndrome |
| NDP | Norrie disease |
| NEB | Nemaline myopathy type 2 |
| NEUROG3 | Diarrhea 4 malabsorptive, congenital |
| NHLRC1 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 2B (Lafora) |
| NPC1 | Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 |
| NPC2 | Niemann-pick disease, type C2 |
| NPHP1 | Joubert syndrome type 4 |
| NPHP3 | Meckel syndrome type 7 |
| NPHP4 | Nephronophthisis type 4 |
| NPHS1 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 1 |
| NPHS2 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 2 |
| NR0B1 | Adrenal hypoplasia, congenital |
| NTRK1 | Insensitivity to pain, congenital, with anhidrosis |
| NUP62 | Striatonigral degeneration, infantile |
| OBSL1 | 3M syndrome 2 |
| OCA2 | Oculocutaneous albinism type 2 |
| OCRL | Lowe Syndrome; Dent disease type 2 |
| OPHN1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Billuart type |
| OTC | Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency |
| PAH | Phenylketonuria |
| PAK3 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 30 |
| PC | Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency |
| PCCA | Propionic acidemia |
| PCDH15 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 23; Usher syndrome, type 1D/F digenic |
| PDHA1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-alpha deficiency |
| PDHB | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-beta deficiency |
| PDHX | Lacticacidemia due to PDX1 deficiency |
| PEX1 | Heimler syndrome type 1 |
| PEX10 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 6A (Zellweger syndrome); Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 6B |
| PEX16 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 8A (Zellweger syndrome); Peroxisome biogenesis disorder, type 8B |
| PEX7 | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 1 |
| PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 deficiency |
| PHF8 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Siderius type |
| PKHD1 | Polycystic kidney disease type 4 |
| PKP1 | Ectodermal dysplasia/skin fragility syndrome |
| PLA2G6 | Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy type 1 |
| PLEC | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy |
| PLOD1 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, kyphoscoliotic type, 1 |
| PLP1 | Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease |
| PMM2 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1A |
| PNPLA1 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 10 |
| PNPO | Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate oxidase deficiency |
| POLG | POLG-related disorders |
| POLR1C | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, type 11; Treacher Collins syndrome 3 |
| POMGNT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 3A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 3B; Type 3C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 15 [LGMDR15]) |
| POMT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 1A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 1B; Type 1C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 11 [LGMD R11]) muscular dystrophy, type 11 [LGMD R11]) |
| POMT2 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy, type 2A (Walker-Warburg syndrome); Type 2B; Type 2C (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 14 [LGMD R14]) muscular dystrophy, type 14 [LGMD R14]) |
| POU1F1 | Pituitary hormone deficiency, combined, type 1 |
| POU3F4 | Deafness, X-linked, type 2 |
| PPT1 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 1 |
| PQBP1 | Renpenning syndrome |
| PRF1 | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, familial, type 2 |
| PRICKLE1 | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic, type 1B |
| PROP1 | Pituitary hormone deficiency, combined, type 2 |
| PRPS1 | Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase (PRS) deficiency |
| PSAP | Combined SAP deficiency |
| PYGL | Glycogen storage disease, type 6 |
| RAB3GAP1 | Warburg micro syndrome; Martsolf syndrome |
| RAB3GAP2 | Warburg micro syndrome; Martsolf syndrome |
| RAD51C | Fanconi anemia, complementation group O |
| RAG1 | Omenn syndrome; Severe combined immunodeficiency, B cell-negative |
| RAG2 | Omenn syndrome; Severe combined immunodeficiency, B cell-negative |
| RAPSN | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence, type 2; Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 11 associated with AChR deficiency |
| RARS2 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 6 |
| RELN | Lissencephaly 2 (Norman-Roberts type) |
| RMRP | Anauxetic dysplasia 1 |
| RNASEH2B | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 2 |
| ROR2 | Robinow syndrome, autosomal recessive |
| RP2 | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 2 X-linked |
| RPGR | Retinitis pigmentosa, type 3 X-linked; Cone-rod dystrophy, X-linked, 1 |
| RPGRIP1 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 6 |
| RPGRIP1L | Joubert syndrome, type 7; Meckel syndrome, type 5; COACH syndrome |
| RS1 | Retinoschisis |
| RTEL1 | Dyskeratosis congenita, autosomal recessive type 5 |
| RYR1 | RYR1 related congenitalmyopathy |
| SACS | Spastic ataxia, Charlevoix-Saguenay, type |
| SBDS | Shwachman-Diamond syndrome |
| SCN4A | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, type 16 |
| SCN9A | Indifference to pain and autosomal recessive hereditary sensory neuropathy type 2D |
| SCNN1B | Pseudohypoaldosteronism, type 1 |
| SCO2 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| SGCA | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 3 (LGMD R3) |
| SGCB | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 4 (LGMD R4) |
| SH3TC2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4C |
| SIL1 | Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome |
| SLC12A1 | Bartter syndrome, type 1 |
| SLC12A6 | Agenesis of the corpus callosum with peripheral neuropathy |
| SLC16A2 | Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome |
| SLC17A5 | Salla disease |
| SLC19A2 | Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome |
| SLC19A3 | Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome, type 2 (biotin-or thiamine-responsive encephalopathy type) |
| SLC25A19 | Microcephaly, Amish type; Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 4 (progressive polyneuropathy type) |
| SLC25A22 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 3 |
| SLC26A2 | Achondrogenesis, type 1B (diastrophic dysplasia) |
| SLC26A4 | Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 4; Pendred syndrome |
| SLC2A2 | Fanconi-Bickel syndrome |
| SLC35A1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2F |
| SLC35C1 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 2C |
| SLC37A4 | Glycogen storage disease, type 1B |
| SLC3A1 | Cystinuria |
| SLC45A2 | Albinism, oculocutaneous, type 4 |
| SLC4A11 | Corneal endothelial dystrophy, autosomal recessive |
| SLC6A8 | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome, type 1 |
| SMN1 | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| SMPD1 | Niemann-Pick disease, type A; Niemann-Pick disease, type B |
| SNAP29 | Cerebral dysgenesis, neuropathy, ichthyosis, and palmoplantar keratoderma syndrome |
| SP110 | Hepatic venoocclusive disease with immunodeficiency |
| SPATA7 | Leber congenital amaurosis, type 3 |
| SRD5A2 | 46,XY disorder of sex development due to 5-alpha-reductase 2 deficiency (pseudovaginal perineoscrotal hypospadias) |
| SRD5A3 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1Q; Kahrizi syndrome |
| ST3GAL5 | Salt and pepper developmental regression syndrome |
| STAR | Lipoid adrenal hyperplasia |
| STIL | Microcephaly, type 7 primary, autosomal recessive |
| STRA6 | Microphthalmia, isolated, with coloboma, type 8 |
| SUOX | Sulfite oxidase deficiency |
| SURF1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4K; Leigh syndrome, due to COX IV deficiency |
| SYN1 | Epilepsy, X-linked, with variable learning disabilities and behavior disorders |
| TCTN1 | Joubert syndrome, type 13 |
| TCTN2 | Joubert syndrome, type 24; ?Meckel syndrome, type 8 |
| TF | Atransferrinemia |
| TGM1 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive, type 1 |
| TH | Segawa syndrome, recessive |
| THOC2 | intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 12 |
| TJP2 | Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, type 4 |
| TMEM138 | Joubert syndrome 16 |
| TMEM216 | Joubert syndrome, type 2; Meckel syndrome, type 2 |
| TMEM237 | Joubert syndrome, type 14 |
| TMEM67 | Joubert syndrome, type 6; Meckel syndrome, type 3; COACH syndrome |
| TNNT1 | Nemaline myopathy, type 5 Amish type |
| TNXB | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classic-like |
| TPK1 | Episodic encephalopathy due to thiamine pyrophosphokinase deficiency |
| TPP1 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, type 2; Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, type 7 |
| TREX1 | Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, type 1 |
| TRIM32 | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 8 (LGMD R8) |
| TSEN2 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2B |
| TSEN34 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2C |
| TSEN54 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 2A; Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 4 |
| TSFM | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency, type 3 |
| TTC21B | Short-rib thoracic dysplasia, type 4 with or without polydactyly |
| TTC8 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome, type 8 |
| TTN | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 10 (LGMDR10); Early-onset myopathy with fatal cardiomyopathy (Salih myopathy) |
| TTPA | Ataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency |
| TYR | Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) type 1A; OCA type 1B |
| UBR1 | Johanson-Blizzard syndrome |
| UNC13D | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, familial, type 3 |
| UPF3B | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic 14 |
| USH1C | Usher syndrome, type 1C; Deafness, autosomal recessive, type 18A |
| USH1G | Usher syndrome, type 1G |
| USH2A | Usher syndrome, type 2A |
| VLDLR | Cerebellar hypoplasia, impaired intellectual development, and dysequilibrium syndrome 1 |
| VPS13B | Cohen syndrome |
| VPS33B | Arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction and cholestasis, type 1 |
| WAS | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; Thrombocytopenia, X-linked |
| WDR62 | Microcephaly, type 2 primary, autosomal recessive, with or without cortical malformations |
| WFS1 | Wolfram syndrome, type 1 |
| WNT7A | Fuhrmann syndrome |
| WRN | Werner syndrome |
| XPA | Xeroderma pigmentosum, group A |
| XPC | Xeroderma pigmentosum, group C |
| ZAP70 | Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, type 2; Immunodeficiency, type 48 |
| ZDHHC9 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Raymond type |
| ZMPSTE24 | Mandibuloacral dysplasia with, type B lipodystrophy |
| ZNF711 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked 97 |

We create happy families
BEOGRAD
Karađorđeva 89
+381 11 414 65 65
info@cord.rs
NOVI SAD
Fruškogorska 24
+381 21 31 01 333
info@cord.rs